绑定如何安装配置你的tomcat5并绑定域名(How to install and configure your tomcat5 and bind domain names)
如何安装配置你的tomcat5并绑定域名How to install andconfigure your tomcat5 and bind domain names
Atomic model of Bohr in section third
Three dimensional teaching objective
1, knowledge and skills
(1) understanding the main content of Bohr' s atomic theory;
(2) understanding the concepts of energy levels, energyquantization, ground state and excited state.
2, process and method: through the study of Bohr theory, tofurther understand the hydrogen spectrum.
3, emotion, attitude and values: cultivate our spirit ofinquiry into science, and develop the spirit of independenceand innovation.
Teaching emphasis: the basic hypothesis of Bohr' s atomictheory.
Teaching difficulties: explanation of hydrogen spectrum byBohr theory.
Teaching methods: teacher elicitation, guidance, studentdiscussion and communication.
(1) introducing new courses
Put questions to
(1) what is the phenomenon of alpha particle scatteringexperiment?
(2) what is the content of the nuclear structure theory?
(3) the contradiction between Lu Sefu' s nuclear structuretheory and classical electromagnetic theory
In order to solve these contradictions, Bohr, a Danishphysicist, proposed his own atomic structure hypothesis in
1913.
(two) take a new course
1. Bohr' s atomic theory
(1) energy level (steady state) hypothesis: the atom can onlyexist in a series of discontinuous energy states. In theseStates, the atom is stable, although electrons move around thenucleus, but do not radiate energy outwards. These states arecalled stationary states. (this hypothesis is proposed foratomic stability)
(2) transition hypothesis: atoms from a steady state (energyEn) transition to another steady state (energy Em) , itsradiation (or absorption) photon frequency, the photon energyis determined by the deviation of the two kinds of stationaryenergy, namely the MERGEFORMAT (EMBED Equation.3 h Planck
(constant) the assumptions for the linear spectrum method)
(3) orbital quantization hypothesis: the different energystates of the atom correspond to the motion of electrons aroundthe nucleus in different circular orbits. The stationary stateof atoms is discontinuous, so the distribution of the possibleorbits of electrons is also discontinuous. (for the nuclearmodel, it is a supplement to the energy level hypothesis)
2. According to the classical electromagnetic theory andNewtonian mechanics, Bohr calculated the possible orbitalradii of hydrogen atoms and the energy (including kineticenergy and potential energy) of electrons moving in variousorbits:
The MERGEFORMAT Equation. 3 orbit radius: EMBED n=1, 2, 3. . . . . .The MERGEFORMAT Equation. 3 energy: EMBED n=1, 2, 3. . . . . .Type R1, E1, representing the first (i. e. from the recentnuclear) movement may orbit radius and electron in the orbitof energy, RN and En respectively represent the article n maytrack radius and electron in the N orbit and the energy of nis a positive integer, called quantum number.
3. Energy level diagram of hydrogen atom
Starting from Bohr' s basic hypothesis, using the classicalelectromagnetism and classical mechanics theory, we cancalculate the possible orbit radius and the correspondingenergy of electrons in hydrogen atom.
(1) the size of the hydrogen atom: the radius of each possibleorbit of the electron of hydrogen atom rn:rn=n2r1,
R1 represents the first line (nearest to the nucleus) . Theradius of the possible orbit is r1=0.53 x 10-10 M
For example: n=2, r2=2. 12 x 10-10 M
(2) energy levels of hydrogen atom:
The energy value En of an atom in its steady state is calledthe energy level of an atom. It can track the correspondingelectron kinetic energy En (including En=E1/n2 n=1 kinetic andpotential energy) , 2, 3,
E1 represents the energy that electrons move on the firstpossible orbit, E1=-13.6eV
Note: when calculating the energy, the electric potentialenergy is zero, the electron is negatively charged, theelectron is negative in the positive charge field, the kineticenergy of the electrons is half of the absolute value of theelectric potential energy, and the total energy is negative.For example: n=2, E2=-3.4eV, n=3, E3=-1.51eV, n=4,
E4=-0.85eV, . . . . . .
The energy level diagram of hydrogen atom is shown:
Explanation of hydrogen spectrum by 4 and Bohr' s Theory
(1) ground state and excited state
Ground state: in the normal state, the atom is in the lowestenergy level, when the electron moves in the nearest orbit fromthe nucleus, which is called the ground state.
Excited state: when the atom is in the higher energy level, theelectron moves in the orbit far away from the nucleus. Thissteady state is called excited state.
Class practice
(1) in the following statements of Bohr' s theory, what iscorrect is (ACD)
A. inherits Rutherford' s atomic model, but introduces quantumhypothesis to atomic energy and electronic orbit
B. agrees with the point of view that the electromagnetic chargeof accelerating motion should be radiated in the classicalelectromagnetic theory
The quantitative relation between the atomic luminescencefrequency and the atomic energy change is established by theenergy transformation and conservation of C.
The two formula of D. Bohr is based on his theory, usingclassical electromagnetic theory and Newtonian mechanics
(2) in the following explanation of Bohr' s theory, the
incorrect statement is (C)
A. atoms can only exist in a series of discontinuous States,each state corresponding to a certain energy
In the B. atom, although the electrons outside the nucleuscontinue to accelerate, they do not radiate energy as long asthe energy state does not change
When the C. atom transitions from one stationary state toanother, it is necessary to radiate a certain frequency ofphotons
Each energy state of the D. atom corresponds to an electronicorbit, and these orbits are discontinuous
(3) according to Bohr' s theory, the greater the quantum numberN in hydrogen atom, the correct in the following statement is(ACD)
The larger the electron orbit radius of A. is, the higher therate of electrons outside the B. nucleus is
The greater the energy level of the C. hydrogen atom, thegreater the potential energy of the outer electrons of the D.nucleus
(4) according to Bohr' s atomic theory, the radius of electronmotion around an atom (D)
A. can take any value, B. can take any value in a certain range
C. can take a series of discontinuous arbitrary values, D. isa series of discontinuous specific values
(5) according to Bohr' s theory, the electrons in ahydrogen atomspontaneously transition from a circular orbit with a radiusof RA to a circular orbit with a radius of Rb, and the knownra>rb is in this process (C)
The A. atom emits a series of photons, and the B. atom absorbsa series of photons
C. atoms emit photons of a certain frequency, and D. atomsabsorb photons of a certain frequency
The center of http://www. zgjhjy.com/.
The motion of electrons around nuclei (with acceleration)The frequency of the radiation electromagnetic wave is equalto the frequency of the operation around the nucleus
Energy reduction, orbital radius reduction, frequencyvari ati on
The electronfalls into theatomicnucleus alongthe spiral line,and the spectrum of the atom should be continuous
(contradiction: actually a discontinuous bright line)The atom is unstable
(contradiction: in fact, atoms are stable)
***[JimiSoft: Unregistered Software ONLY Convert Part Of File!Read Help To Know How To Register. ]***
- 绑定如何安装配置你的tomcat5并绑定域名(How to install and configure your tomcat5 and bind domain names)相关文档
- 检索域名绑定
- 汝南县人民检察院采购电子检务设备项目
- 济源职业技术学校2016年度电子商务专业实训基地建设方案
- 投标前请认真阅读,如投标即
- 洛阳市域名绑定
- 采购项目编号:以系统自动生成为准(详见采购公告)
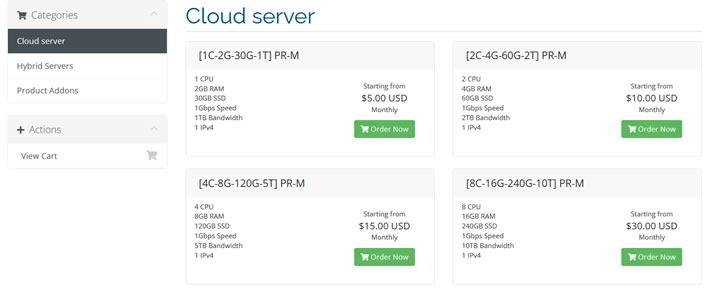
HaloCloud:日本软银vps100M/200M/500M带宽,,¥45.00元/月
halocloud怎么样?halocloud是一个于2019下半年建立的商家,主要提供日本软银VPS,广州移动VDS,株洲联通VDS,广州移动独立服务器,Halo邮局服务,Azure香港1000M带宽月抛机器等。日本软银vps,100M/200M/500M带宽,可看奈飞,香港azure1000M带宽,可以解锁奈飞等流媒体,有需要看奈飞的朋友可以入手!点击进入:halocloud官方网站地址日本vp...
Virmach款低价VPS可选可以选择多个机房,新增多款低价便宜VPS主机7.2美元起
Virmach商家我们是不是比较熟悉?速度一般,但是人家价格低,而且机房是比较多的。早年的时候有帮助一个有做外贸也许需要多个机房且便宜服务商的时候接触到这个商家,有曾经帮助够买过上百台这样的低价机器。这里需要提醒的,便宜但是速度一般,尤其是中文业务速度确实不快,如果是外贸业务,那肯定是没有问题。这几天,我们有看到Virmach推出了夏季优惠促销,VPS首年8折,最低年付仅7.2美元,多机房可选,如...

PacificRack 下架旧款方案 续费涨价 谨慎自动续费
前几天看到网友反馈到PacificRack商家关于处理问题的工单速度慢,于是也有后台提交个工单问问,没有得到答复导致工单自动停止,不清楚商家最近在调整什么。而且看到有网友反馈到,PacificRack 商家的之前年付低价套餐全部下架,而且如果到期续费的话账单中的产品价格会涨价不少。所以,如果我们有需要续费产品的话,谨慎选择。1、特价产品下架我们看到他们的所有原来发布的特价方案均已下架。如果我们已有...
-
软银孙正义孙正义和马云什么关系朱祁钰和朱祁镇哪个好大家怎么看明英宗和明代宗浮动利率和固定利率哪个好贷款选择浮动利率还是固定利率ps软件哪个好Photoshop哪个软件好用点?英语词典哪个好英语词典哪种更好啊?无纺布和熔喷布口罩哪个好医用 口罩里面是无纺布好还是过滤纸好红茶和绿茶哪个好红茶和绿茶,哪个好?qq空间登录界面强行进入别人qq空间qqkj空间登录怎么限制qq空间登录.电信10000宽带测速电信宽带速度