anddoesn[小学]tcp-ip day4 国外大学课件
TCP/IP
ARP c ontinued,ARP c ache pois oning
ARP resolution–the details
First, we' ll look at the format of an ARP message (see text, or look it up ongoogle) .
The protocol has three aspects: it specifies what a requester is to do, what areceiver is to do, and what a responder is to do. A requester is a machine thatsends an ARP request, a receiver is a machine that receives any ARP message, anda responder is a machine that sends an ARP reply.
On our Ethernet network, here' s the process in detail; for a requester:
Create an ARP message:
1. Set HW type to ' 1' (for Ethernet)
2. Set Protocol type to 080016 (for IP)
3. Set HLEN to 6 (6x8=48 bits)
4. Set PLEN to 4 (4x8=32 bits)
5. Set OPERATION to 1 (for ARP request)
6. Fill in SENDER' s HW ADD
7. Fill in SENDER' s PROT ADD
8. Set TARGET HW ADD to 0 (doesn' t know)
9. Fill in TARGET PROT ADD.
Broadcast the ARP message in an Ethernet frame.
For a receiver (of either an ARP request or reply) or responder
Extract the ARP request
If the SENDER' s PROT address in in my cache, update it with the SENDER' s HWaddress and reset the timer on that pairing
If the TARGET PROT address is identical with my IP address, carry on, otherwise,quit
Update my cache (again) , regardless of wh'ether an entry exists for that PROTaddress. (all this is done even if it isn t a request)
[ [Here it would be possible for the arp request to contain a protocol addressidentical with the protocol address of the target. We noted that Windowsoperating systems detect this, and make a note on 'the console. I tested Linux,and i't simply ignores the arp request, i. e. , doesn t generate a reply, anddoesn t update its arp cache. ] ]
If the OPERATION is a request, carry on; otherwise quit.
Fill in TARGET HW address with my Ethernet address, swap SENDER and TARGETaddresses, and set OPERATION to 2
Encapsulate ARP reply in a frame addressed to TARGET HW address.
QUESTIONS
Why does the ARP request recipient try to update its cache twice before evenexamining whether the message is a request? And once before even examiningwhether it is the intended recipient ?
( ( 1st time: save on traffic ) )
( ( 2nd: save repeating the process in reverse ) )
Gratuitous ARP
One other application of ARP that I' ll mention briefly is gratuitous ARP. Some OSs employs ARP to make sure that there are not duplicate IP addresses onthe physical network. (In fact OpenBSD does this. )
It broadcasts an ARP looking for the HW address of itself, i.e. , of its IPaddress.
If it receives a reply, it knows there is another host with its IP address, andputs a message on the console.
ARP Cache Poisoning
- ARP is a protocol which generates mappings between IP addresses and hardwareaddresses
- The basic idea, you will recall, is as follows:
- |A|-------|B|
- Host A wants to talk to host B, but A doesn’ t know B’ s HW addr
- A sends an ARP request to B, containing a mapping between A’ s HW and IPaddr
- B caches this mapping, and returns a reply with its mapping
- Communication proceeds
- There are three aspects to ARP cache poisoning that I want to discuss: (1)
What is it? (2) How do you do it? (3) Why do it?
- (1) ARP cache poisoning is when one machi’ne on a network, s’ay C, causes afalse entry to be placed in another host s, for example C s, ARP cache.- (2) It is very easy to poison ARP caches, and operating systems have triedvarious methods to protect against it, the main one being the creation of an
incomplete entry in the arp cache, and updating according to the steps aboveonly if that incomplete entry exists; this will go some way to protectingagainst unsolicited arp replies. ‘ However’ , this creates a race condition,poisoning i‘s still possible’by spaming unsolicited arp replies, in thehopes of winning the race against legitimate, solicited arp replies.
(3) Poisoning Effects
ARP cache poisoning can be used in various ways, the three most fundamentalof which are:
- (a) Eavesdropping
- Now suppose that an attacker, host C, wants to eavesdrop on communicationbetween host A and host B, but that the LAN is switched Ethernet. (How doesswitched Ethernet work?)
- |A|--------|B|
- |
- |C|
- If’ C could convince A that B’ s HW addr is C’ s, and could convince B thatA s is also C, then all traffic from B to A, and vice versa, would go to C.- Moreover, if C turned on forwarding, and had the correct HW-IP mappings, Cwould in effect become a kind of router between A and B, and would
consequently have access to all communication between A and B.
- The effect of this attack would be the disclosure of potentially confidentialinformation.
- (b) Denial of service
- On the other hand, perhaps C is not interested in eavesdropping, but wouldrather deny A and B the ability to communicate with one another.
- In this case, it would suffice for C to poison A’ s and B’ s caches withmappings eit’her to non-existent hardware addresses, or alternately, again useits own – C s – HW address, and simply not forward (the former makes iteasier for the attacker to hide his/her tracks) .
- (c) Hijacking
- Another possibility is that C is not interested in eavesdropping or DoS, butrather, wants to take over one end of the conversation.
- This would be a kind of combination of the previous two attacks: First, Cwould need to eavesdrop using the method previously outlined.
- Then, after (e.g. ) authentication, C performs a DoS on A, and takes over A’ srole in this 2-way conversation.o (Another example, besides authentication, that A might wait until thetwo hosts are communicating, is in order to sample TCP sequence andacknowledgement numbers, which is necessary in order to successfullyhijack a TCP session. This will make more sense when we come to TCP. )- This is called session hijacking (normally TCP sessions) , and there arevariations on this theme. E.g. , C could maintain the connection between Aand B, yet insert data into the communication channel.
- ARP Poisoning: not just a LAN issue
- These attacks are not limited to hosts on a single LAN. In fact, provided wehave LAN access to anynetwork on the path between A and B, these attacks arepossible.
- Examples:
- C
- |------------
- | |
- A B
- Here we merely poison A and R1.
- C
- |------------R1-----Internet----
- | |
- A B
- Poison B and R2
- C
- |------------R1-----Internet-----R2----R3---------|
- | |
- A B
- Poison R2 and R3
- anddoesn[小学]tcp-ip day4 国外大学课件相关文档
- lecture[说明]tcp-ip_day2 国外大学课件
- 美国[攻略]国外ip地址
- 产权IP版权交易平台如何进行融资交易,国外有哪些模式值得借鉴
Virtono:圣何塞VPS七五折月付2.2欧元起,免费双倍内存
Virtono是一家成立于2014年的国外VPS主机商,提供VPS和服务器租用等产品,商家支持PayPal、信用卡、支付宝等国内外付款方式,可选数据中心共7个:罗马尼亚2个,美国3个(圣何塞、达拉斯、迈阿密),英国和德国各1个。目前,商家针对美国圣何塞机房VPS提供75折优惠码,同时,下单后在LET回复订单号还能获得双倍内存的升级。下面以圣何塞为例,分享几款VPS主机配置信息。Cloud VPSC...
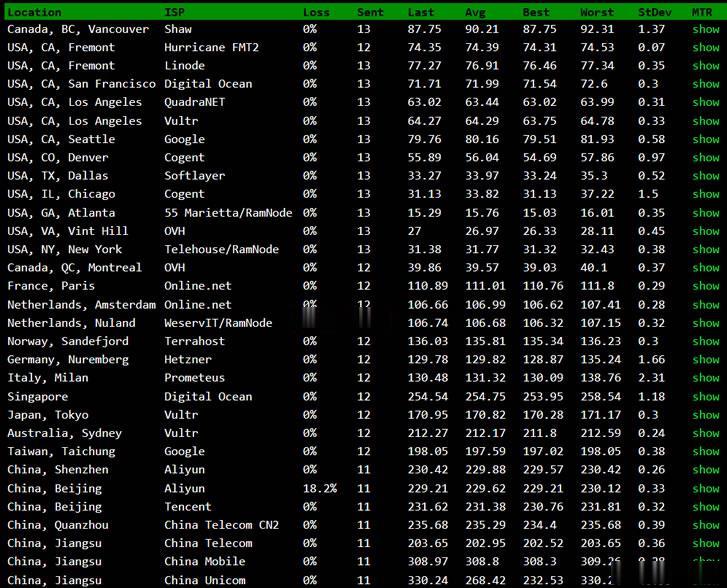
BuyVM新设立的迈阿密机房速度怎么样?简单的测评速度性能
BuyVM商家算是一家比较老牌的海外主机商,公司设立在加拿大,曾经是低价便宜VPS主机的代表,目前为止有提供纽约、拉斯维加斯、卢森堡机房,以及新增加的美国迈阿密机房。如果我们有需要选择BuyVM商家的机器需要注意的是注册信息的时候一定要规范,否则很容易出现欺诈订单,甚至你开通后都有可能被禁止账户,也是这个原因,曾经被很多人吐槽的。这里我们简单的对于BuyVM商家新增加的迈阿密机房进行简单的测评。如...
hostodo:2021美国独立日7折优惠促销NVMe硬盘的VPS,低至$13/年,还送DirectAdmin授权
7月4日是美国独立日,大致就是国庆节的意思吧。hostodo今年提前搞了个VPS大促销活动,4款便宜VPS,相当于7折,续费不涨价,本次促销不定时,不知道有多少货,卖完为止。VPS基于KVM虚拟,NVMe阵列,1Gbps带宽,自带一个IPv4+/64 IPv6,solusvm管理,送收费版DirectAdmin授权,VPS在用就有效! 官方网站:https://www.hostodo.com ...
-
"中科院重庆绿色智能技术研究院采购供应商信息登记表"directional163游戏ios点击ipad支持ipad张女士苹果5化学品安全技术说明书css下拉菜单如何使用HTML和CSS制作下拉菜单ipad上网新买的ipad怎么用。什么装程序 怎么上网ms17-010win1038度古贝春珍藏10价格?