parasympathetic7788k.com
7788k.com 时间:2021-03-17 阅读:()
IntJClinExpMed2020;13(10):7787-7793www.
ijcem.
com/ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0116166OriginalArticleAnalysisofneurogenicelectrocardiographicchangesinacutestrokepatientsWeidaGuo1,LeiLiu2,FangWen1,YuechunShen31ElectrocardiographicRoom,Departmentsof2Neurology,3Cardiovasology,TheFirstAffiliatedHospitalofGuangzhouMedicalUniversity,Guangzhou,GuangdongProvince,ChinaReceivedJune12,2020;AcceptedJuly19,2020;EpubOctober15,2020;PublishedOctober30,2020Abstract:Objective:Ouraimwastoexploretheneurogenicelectrocardiographic(ECG)abnormalitiesinacutestrokepatientsandtheECGcharacteristicsindifferenttimeperiods,soastoprovidesupportforclinicaldataofECGchar-acteristicsinstrokepatients.
Methods:Inthisretrospectivestudy,werecruited260patientswithacuteneurogenicstrokewhoreceivedtreatmentduringJanuarytoDecember2019.
Accordingtothestroketype,wedividedthemintocerebralhemorrhage(CH)groupandcerebralischemia(CI)group(n=130each).
TheECGchangesinallpatientsweremonitoredduringtheacutephase(within48hours)andrecoveryphase(2weeksaftertreatment),andthetypicalabnormalitiesoftheECGineachgroupwereanalyzed.
Results:ThetotalincidenceofECGabnormalitiesintheCHgroup(79.
23%,103/130)wassignificantlyhigherthanthatintheCIgroup(68.
46%,89/130;P0.
05),suggestingthetwogroupsarecomparable.
SeeTable1.
ECGabnormalitiesintheacutephaseECGchangesinacutestrokepatients7790IntJClinExpMed2020;13(10):7787-7793ComparisonofincidencesofECGabnormali-tiesintheacutephaseTherewerenosignificantdifferencesintheincidencesofST-Tdepression,Qwaveabnor-malities,QTintervalprolongationandsignifi-cantUwavebetweenthetwogroups(allP>0.
05),whileincidencesofPwaveabnormali-tiesandarrhythmiaweresignificantlyhigherintheCHgroupthanintheCIgroup(P=0.
006andP=0.
041,respectively).
SeeTable3.
Furthermore,asFigure3shows,thecommonECGabnormalitiesintheacutephasewerePwaveabnormalities,ST-Tdepressionandarrhythmia;significantdifferencesintheinci-dencesofPwaveabnormalitiesandarrhythmiawerefoundbetweenthetwogroups(bothP<0.
05).
ComparisonofincidencesofECGabnormali-tiesandcardiacsequelaebetweentheacuteandrecoveryphaseTheCHgroupshowedamoredownwardtrendintheincidenceofECGabnormalitiesintherecoveryphasethanintheacutephase,withthemostsignificantdecreaseintheincidenceofST-Tdepression(P<0.
01),SeeTable5.
TheCIgroupalsoshowedamoredownwardtrendintheincidenceofECGabnormalitiesintherecoveryphasethanintheacutephase,withthemostsignificantdecreasesinincidencesofST-Tdepressionandarrhythmiaintherecoveryphase(P=0.
002andP=0.
035,respectively).
SeeTable6.
TheresultsindicatethatECGabnormalitiesinstrokepatientsatdifferenttimepointsarereversibleandcanreturntonor-malgraduallyaftertreatment.
Additionally,theincidenceofCHDaftertreat-mentintheCIgroup(22.
47%)wassignificantlylowerthanthatintheCHgroup(42.
72%)aftertreatment(P=0.
027).
SeeTable7.
Theresult,combinedwiththeECGfindingsinTables5and6intherecoveryphase,revealsthatCHpatientswithPwaveabnormalitiesandST-Tdepressionintheacutephaseshowacompar-ativelyhighincidenceofCHDaftertreatment.
DiscussionStrokeisoneofthemostcommonCCVDsinclinicalpractice,whichseverelyendangerstheTable3.
ComparisonofincidencesofECGabnormalitiesintheacutephase(n,%)ECGabnormalitiesCHgroupCIgroupχ2PPwaveabnormalities69(53.
08%)47(36.
15%)7.
5340.
006ST-Tdepression59(45.
38%)61(46.
92%)0.
0620.
804Arrhythmia58(44.
62%)42(32.
31%)4.
1600.
041Qwaveabnormalities4(3.
08%)4(3.
08%)0.
0001.
000QTintervalprolongation5(3.
85%)4(3.
08%)0.
0001.
000SignificantUwave4(3.
08%)2(1.
54%)0.
1710.
680Note:CI:cerebralischemia;CH:cerebralhemorrhage;ECG:electrocardio-graphic.
Table4.
Comparisonofincidenceofauto-nomicdysfunction(n,%)GroupCasesAutonomicdysfunctionχ2PCIgroup13019(14.
62%)4.
1220.
042CHgroup13032(24.
62%)Note:CI:cerebralischemia;CH:cerebralhemorrhage.
Figure3.
ComparisonofincidencesofECGabnor-malitiesintheacutephase.
ComparedwiththeCHgroup,*P<0.
05;**P<0.
01.
CI:cerebralischemia;CH:cerebralhemorrhage;ECG:electrocardiographic.
ItcanbeseenfromTable4thattheincidenceofautonomicdys-functionwasmarkedlyhigherintheCHgroupthanintheCIgroup(P=0.
042).
AsshowninTable3,therewasanextremelysignificantdifferenceintheincidenceofPwaveabnormalitiesbetweenthetwogroups.
TheresultssuggestthatPwaveabnormalitiesinacutephasemaybeassociatedwithautonomicdysfunction,whichpro-videsacertainclinicalreference.
ECGchangesinacutestrokepatients7791IntJClinExpMed2020;13(10):7787-7793healthandlivesofpatients.
Forstrokepatients,effectiveclinicaljudgmentandvaliddrugtreat-mentareofgreatimportancetotherehabilita-tionandprognosis[11-13].
ApreviousstudyreportedthatneurogenicECGabnormalitiesmostlyoccurredintheacutestrokepatients,particularlyinpatientswithhemorrhagicstroke,within2daysafteronsetwithanincidencerateof60-90%[14].
ECGwaveformabnormalitiesmayalsolastformorethan2weeksinstrokepatients,anduptoabout4weeksinafewpatients[15].
Inthisstudy,wemonitoredacuteECGchangesinpatientswithacuteneurogenicstrokeandtheresultsshowedthattheinci-denceofECGabnormalitiesinallpatientswas73.
85%,andtheincidenceofECGabnor-malitiesinhemorrhagicstrokepatientswas79.
23%,confirmingahighincidenceofstroketionrate(46.
15%)amongECGabnormalities;thehighlyimproveddetectionrateduringrecov-erysuggeststhatECGabnormalitiesinstrokepatientsarereversibleandcanbebacktonor-malgraduallythroughtreatment.
Inlinewithourstudy,Sudhishetal.
alsoreportedthatpatientswithacuteischemicstrokeshowedasignificantST-Tdepressionwithgradualrecov-ery[18].
Astoarrhythmia,severearrhythmia,especiallytorsadesdepointes,causedbyneu-rogenicstrokemightleadtodeath.
Thismaybebecauseparasympatheticregulationwaseasilyaffectedbycerebralfunctionalimpairment,thuscausingarrhythmia,orcardiovasculardys-functionresultingfromintracranialhemorrhageledtocardiacdamage.
Therefore,it'sessentialtomonitorPwaveandheartrhythmduringrecovery,withparticularfocusontheoccur-Table5.
ComparisonofincidencesofECGabnormalitiesbe-tweentheacuteandrecoveryphaseinCHgroup(n,%)ECGabnormalitiesAcutephaseRecoveryphaseχ2PPwaveabnormalities69(53.
08%)55(42.
31%)3.
0220.
082ST-Tdepression59(45.
38%)33(25.
38%)11.
3720.
001Arrhythmia58(44.
62%)47(36.
15%)1.
9330.
164Qwaveabnormalities4(3.
08%)3(2.
31%)0.
1470.
702QTintervalprolongation5(3.
85%)3(2.
31%)0.
1290.
720SignificantUwave4(3.
08%)2(1.
54%)0.
1710.
680Note:CH:cerebralhemorrhage;ECG:electrocardiographic.
Table6.
ComparisonofincidencesofECGabnormalitiesbe-tweentheacuteandrecoveryphaseinCIgroup(n,%)ECGabnormalitiesAcutephaseRecoveryphaseχ2PPwaveabnormalities47(36.
15%)33(25.
38%)3.
5390.
060ST-Tdepression61(46.
92%)37(28.
46%)9.
4330.
002Arrhythmia42(32.
31%)27(20.
77%)4.
4390.
035Qwaveabnormalities4(3.
08%)1(0.
77%)0.
8160.
366QTintervalprolongation4(3.
08%)2(1.
54%)0.
1710.
680SignificantUwave2(1.
54%)0(0%)0.
5040.
478Note:CI:cerebralischemia;ECG:electrocardiographic.
Table7.
Comparisonofcardiovasculardiseaseincidence(n,%)GroupCasesofECGabnormalitiesintheacutephaseCasesofCHDaftertreatmentχ2PCIgroup8928(31.
46%)4.
9170.
027CHgroup10344(42.
72%)Note:CI:cerebralischemia;CH:cerebralhemorrhage;ECG:electrocardiographic;CHD:coronaryheartdisease.
combinedwithcardiacdiseas-es.
Moreover,previousstudiesofECGchangesinstrokepatientshaveunveiledthatECGchangesareassociatedwithstrokelocationandrecov-erystatus,andstrokepatientsweremorelikelytodevelopcar-diacsequelae,e.
g.
,thosewithPwaveabnormalitiesandsignifi-cantST-Tdepressionintheacutephasehaveahighrateofcardiovascularsequelae[16,17].
Inthisstudy,ECGchangeswe-reanalyzedinpatientswithacutestrokeandtheabnormalwaveformsmainlyconsistedofPwaveabnormalities,ST-Tde-pressionandarrhythmia.
AstoPwaveabnormalities,itmainlyreferredtohighamplitudePwave,whoseincidencerateinhemorrhagestrokepatientswasupto53.
08%.
Intherecov-eryphase(2weeksaftertreat-ment),Pwaveamplitudegradu-allydecreased,whilenosignifi-cantdifferencewasfoundbe-tweenPwaveabnormalitiesintheacuteandrecoveryphase,indicatingthatalongerobser-vationtimemaybeneeded.
AstoST-Tdepression,theresultsdemonstratedaflatorinvertedTwaveandthehighestdetec-ECGchangesinacutestrokepatients7792IntJClinExpMed2020;13(10):7787-7793renceofcardiovasculardiseases.
Inthisstudy,weshowedthattheincidencesofPwaveabnor-malitiesandarrhythmiawerehigherintheCHgroupthantheCIgroupintherecoveryphase,whilenosignificantchangewasobservedbetweentheincidencesduringtheacuteandrecoveryphase.
Furthermore,thisstudydem-onstratedmarkedlyhigherincidencesofCHDandautonomicdysfunctionintheCHgroupthantheCIgroup.
Thismaybebecausehypo-thalamicinjuryresultingfromhemorrhagestrokeledtoactivationofthesympathetic-adrenalsystem.
Hence,wespeculatedthattheECGchangesmaybeoneoftheauxiliaryindica-torsforassessingtherehabilitationstatusofpatientsandtheriskofsequelae.
Currently,thespecificcausesandmechanismsofECGchangesinacutestrokepatientsarestillnotveryclear.
Somephysicianscientistsbelievethatitmayberelatedtothestructureofdiencephalonandbrainstem[19,20].
ThechangesinreleaseofmediatorscausedbyalterationsofsympatheticandvagalnervoustensionresultedinECGabnormalities.
Forexample,theanteriorcranialfossamaycauseECGchanges,andcerebellartonsillardamagemaycauseinfarct-likeECGchanges[21].
Severallimitationsstillremaininthisstudythoughwehaveachievedcertainpositiveresults.
Thediseasetypeswerenotvarious,andthemonitoringtimewaslimitedintherecoveryphase,somorestudiesareneededtogetamorepreciseconclusioninthefuture.
Insummary,wereportahighincidenceofECGabnormalitiesinacuteneurogenicpatients,andareducedabnormalityrateinmostpatientsduringrecoveryaftertreatment.
CHpatientsshowahigherincidenceofabnormalitiesthanCIpatients,andCHpatientswithPwaveabnor-malitiesandsignificantST-Tdepressionintheacutephaseshowacomparativelyhighinci-denceofcardiovascularsequelae.
Hence,ECGmonitoringhascertainclinicalsignificanceforclinicalobservationandprognosisinpatientswithacuteneurogenicstroke.
DisclosureofconflictofinterestNone.
Addresscorrespondenceto:YuechunShen,De-partmentofCardiovasology,TheFirstAffiliatedHospitalofGuangzhouMedicalUniversity,No.
151YanjiangWestRoad,Guangzhou510120,Guang-dongProvince,China.
Tel:+86-020-83063091;E-mail:shenyuechung1ya@163.
comReferences[1]LiuJ,ZhengL,ChengY,ZhangS,WuB,WangD,ZhangS,TaoW,WuSandLiuM.
Trendsinoutcomesofpatientswithischemicstroketreatedbetween2002and2016:insightsfromaChinesecohort.
CircCardiovascQualOutcomes2019;12:e005610.
[2]FeiginVL,KrishnamurthiRV,ParmarP,Norrv-ingB,MensahGA,BennettDA,Barker-ColloS,MoranAE,SaccoRL,TruelsenT,DavisS,Pan-dianJD,NaghaviM,ForouzanfarMH,NguyenG,JohnsonCO,VosT,MeretojaA,MurrayCJandRothGA.
Updateontheglobalburdenofischemicandhemorrhagicstrokein1990-2013:theGBD2013study.
Neuroepidemiolo-gy2015;45:161-176.
[3]GuoX,LiZ,ZhouY,YuS,YangH,ZhengL,LiuYandSunY.
MetabolicprofileforpredictionofischemicstrokeinChinesehypertensivepopu-lation.
JStrokeCerebrovascDis2019;28:1062-1069.
[4]LiuM,WuB,WangWZ,LeeLM,ZhangSHandKongLZ.
StrokeinChina:epidemiology,pre-vention,andmanagementstrategies.
LancetNeurol2007;6:456-464.
[5]KongJ,XieLX,LiuPL,JingM,HUWHandZhangSQ.
Effectsofaspirinandclopidogrelontheriskofuppergastrointestinalbleedinginpatientswithcardiovascularandcerebrovas-culardiseases.
ZhongguoShengHuaYaoWuZaZhi2017;37:153-155.
[6]ShenM,NiuXandWangL.
Applicationofbloodlipidlevelmonitoringindiagnosisandtherapyofcardiovascularandcerebrovasculardiseases.
ZhonghuaJianYanYiXueZaZhi2018;41:893-896.
[7]FreedmanB,SchnabelRandCalkinsH.
Op-portunisticelectrocardiogramscreeningforatrialfibrillationtopreventstroke.
JAMACardi-ol2019;4:91-92.
[8]BobingerT,KallmunzerB,KoppM,KurkaN,ArnoldM,HeiderS,SchwabSandKohrmannM.
DiagnosticvalueofprehospitalECGinacutestrokepatients.
Neurology2017;88:1894-1898.
[9]WenZJ,WuC,ShenMF,MeiBBandDingJP.
Therelationshipbetweenstrokelocationandpost-strokedepressioninfirst-everstrokepa-tients:ameta-analysis.
ChongqingMed2017;46:2677-2682.
[10]CerasuoloJO,CiprianoLEandSposatoLA.
Thecomplexityofatrialfibrillationnewlydiagnosedafterischemicstrokeandtransientischemicattack:advancesanduncertainties.
CurrOpinNeurol2017;30:28-37.
ECGchangesinacutestrokepatients7793IntJClinExpMed2020;13(10):7787-7793[11]FengX,LiY,WangY,LiL,LittlePJ,XuSWandLiuS.
Danhonginjectionincardiovascularandcerebrovasculardiseases:pharmacologicalactions,molecularmechanisms,andthera-peuticpotential.
PharmacolRes2019;139:62-75.
[12]GuHQ,RaoZZ,YangX,WangCJ,ZhaoXQ,WangYL,LiuLP,WangCY,LiuC,LiH,LiZX,XiaoRPandWangYJ.
Useofemergencymedi-calservicesandtimelytreatmentamongisch-emicstroke.
Stroke2019;50:1013-1016.
[13]SilsbyM,DumaSR,FoisAF,YinYWK,KoryznaJ,MahantN,EvansAandFungVSC.
Timetoacutestroketreatmentin-hourswasmorethanhalvedaftertheintroductionoftheHel-sinkiModelatWestmeadHospital.
InternMedJ2019;49:1386-1392.
[14]RuthiragoD,JulayanontP,TantrachotiP,KimJandNugentK.
Cardiacarrhythmiasandabnor-malelectrocardiogramsafteracutestroke.
AmJMedSci2016;351:112-118.
[15]StoneJ,Mor-AviV,ArdeltAandLangRM.
Fre-quencyofinvertedelectrocardiographictwaves(cerebraltwaves)inpatientswithacutestrokesandtheirrelationtoleftventricularwallmotionabnormalities.
AmJCardiol2018;121:120-124.
[16]KumarS,SharmaGDandDograVD.
Astudyofelectrocardiogramchangesinpatientswithacutestroke.
IntJResMedSci2016;4:2930-2937.
[17]HsiehCY,LinHJ,HuYHandSungSF.
Strokeseveritymaypredictcausesofreadmissionwithinoneyearinpatientswithfirstischemicstrokeevent.
JNeurolSci2017;372:21-27.
[18]SudhishG,MoorthySandMadhavanK.
Astudyofelectrocardiographicabnormalitiesinpatientswithacutecerebrovascularevents.
JClinDiagnRes2019;13:13-16[19]Martin-GallegoA,Gonzalez-GarciaL,Carrasco-BrenesA,Segura-Fernandez-NoguerasM,Delgado-BabianoA,Ros-SanjuanA,Romero-MorenoL,Dominguez-PaezM,Dawid-MilnerMSandArraez-SanchezMA.
Brainstemandautonomicnervoussystemdysfunction:aneu-rosurgicalpointofview.
ActaNeurochirSuppl2017;124:221-229.
[20]OkunlolaAI,OlowoyoP,OkunlolaCKandBaba-lolaOF.
Posteriorcirculationstrokemimickingapontomedullarybrainstemlesion:acasere-port.
InterdiscipNeurosurg2019;18:100491.
[21]KatsanosAH,KorantzopoulosP,TsivgoulisG,KyritsisAP,KosmidouMandGiannopoulosS.
Electrocardiographicabnormalitiesandcardi-acarrhythmiasinstructuralbrainlesions.
IntJCardiol2013;167:328-334.
ijcem.
com/ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0116166OriginalArticleAnalysisofneurogenicelectrocardiographicchangesinacutestrokepatientsWeidaGuo1,LeiLiu2,FangWen1,YuechunShen31ElectrocardiographicRoom,Departmentsof2Neurology,3Cardiovasology,TheFirstAffiliatedHospitalofGuangzhouMedicalUniversity,Guangzhou,GuangdongProvince,ChinaReceivedJune12,2020;AcceptedJuly19,2020;EpubOctober15,2020;PublishedOctober30,2020Abstract:Objective:Ouraimwastoexploretheneurogenicelectrocardiographic(ECG)abnormalitiesinacutestrokepatientsandtheECGcharacteristicsindifferenttimeperiods,soastoprovidesupportforclinicaldataofECGchar-acteristicsinstrokepatients.
Methods:Inthisretrospectivestudy,werecruited260patientswithacuteneurogenicstrokewhoreceivedtreatmentduringJanuarytoDecember2019.
Accordingtothestroketype,wedividedthemintocerebralhemorrhage(CH)groupandcerebralischemia(CI)group(n=130each).
TheECGchangesinallpatientsweremonitoredduringtheacutephase(within48hours)andrecoveryphase(2weeksaftertreatment),andthetypicalabnormalitiesoftheECGineachgroupwereanalyzed.
Results:ThetotalincidenceofECGabnormalitiesintheCHgroup(79.
23%,103/130)wassignificantlyhigherthanthatintheCIgroup(68.
46%,89/130;P0.
05),suggestingthetwogroupsarecomparable.
SeeTable1.
ECGabnormalitiesintheacutephaseECGchangesinacutestrokepatients7790IntJClinExpMed2020;13(10):7787-7793ComparisonofincidencesofECGabnormali-tiesintheacutephaseTherewerenosignificantdifferencesintheincidencesofST-Tdepression,Qwaveabnor-malities,QTintervalprolongationandsignifi-cantUwavebetweenthetwogroups(allP>0.
05),whileincidencesofPwaveabnormali-tiesandarrhythmiaweresignificantlyhigherintheCHgroupthanintheCIgroup(P=0.
006andP=0.
041,respectively).
SeeTable3.
Furthermore,asFigure3shows,thecommonECGabnormalitiesintheacutephasewerePwaveabnormalities,ST-Tdepressionandarrhythmia;significantdifferencesintheinci-dencesofPwaveabnormalitiesandarrhythmiawerefoundbetweenthetwogroups(bothP<0.
05).
ComparisonofincidencesofECGabnormali-tiesandcardiacsequelaebetweentheacuteandrecoveryphaseTheCHgroupshowedamoredownwardtrendintheincidenceofECGabnormalitiesintherecoveryphasethanintheacutephase,withthemostsignificantdecreaseintheincidenceofST-Tdepression(P<0.
01),SeeTable5.
TheCIgroupalsoshowedamoredownwardtrendintheincidenceofECGabnormalitiesintherecoveryphasethanintheacutephase,withthemostsignificantdecreasesinincidencesofST-Tdepressionandarrhythmiaintherecoveryphase(P=0.
002andP=0.
035,respectively).
SeeTable6.
TheresultsindicatethatECGabnormalitiesinstrokepatientsatdifferenttimepointsarereversibleandcanreturntonor-malgraduallyaftertreatment.
Additionally,theincidenceofCHDaftertreat-mentintheCIgroup(22.
47%)wassignificantlylowerthanthatintheCHgroup(42.
72%)aftertreatment(P=0.
027).
SeeTable7.
Theresult,combinedwiththeECGfindingsinTables5and6intherecoveryphase,revealsthatCHpatientswithPwaveabnormalitiesandST-Tdepressionintheacutephaseshowacompar-ativelyhighincidenceofCHDaftertreatment.
DiscussionStrokeisoneofthemostcommonCCVDsinclinicalpractice,whichseverelyendangerstheTable3.
ComparisonofincidencesofECGabnormalitiesintheacutephase(n,%)ECGabnormalitiesCHgroupCIgroupχ2PPwaveabnormalities69(53.
08%)47(36.
15%)7.
5340.
006ST-Tdepression59(45.
38%)61(46.
92%)0.
0620.
804Arrhythmia58(44.
62%)42(32.
31%)4.
1600.
041Qwaveabnormalities4(3.
08%)4(3.
08%)0.
0001.
000QTintervalprolongation5(3.
85%)4(3.
08%)0.
0001.
000SignificantUwave4(3.
08%)2(1.
54%)0.
1710.
680Note:CI:cerebralischemia;CH:cerebralhemorrhage;ECG:electrocardio-graphic.
Table4.
Comparisonofincidenceofauto-nomicdysfunction(n,%)GroupCasesAutonomicdysfunctionχ2PCIgroup13019(14.
62%)4.
1220.
042CHgroup13032(24.
62%)Note:CI:cerebralischemia;CH:cerebralhemorrhage.
Figure3.
ComparisonofincidencesofECGabnor-malitiesintheacutephase.
ComparedwiththeCHgroup,*P<0.
05;**P<0.
01.
CI:cerebralischemia;CH:cerebralhemorrhage;ECG:electrocardiographic.
ItcanbeseenfromTable4thattheincidenceofautonomicdys-functionwasmarkedlyhigherintheCHgroupthanintheCIgroup(P=0.
042).
AsshowninTable3,therewasanextremelysignificantdifferenceintheincidenceofPwaveabnormalitiesbetweenthetwogroups.
TheresultssuggestthatPwaveabnormalitiesinacutephasemaybeassociatedwithautonomicdysfunction,whichpro-videsacertainclinicalreference.
ECGchangesinacutestrokepatients7791IntJClinExpMed2020;13(10):7787-7793healthandlivesofpatients.
Forstrokepatients,effectiveclinicaljudgmentandvaliddrugtreat-mentareofgreatimportancetotherehabilita-tionandprognosis[11-13].
ApreviousstudyreportedthatneurogenicECGabnormalitiesmostlyoccurredintheacutestrokepatients,particularlyinpatientswithhemorrhagicstroke,within2daysafteronsetwithanincidencerateof60-90%[14].
ECGwaveformabnormalitiesmayalsolastformorethan2weeksinstrokepatients,anduptoabout4weeksinafewpatients[15].
Inthisstudy,wemonitoredacuteECGchangesinpatientswithacuteneurogenicstrokeandtheresultsshowedthattheinci-denceofECGabnormalitiesinallpatientswas73.
85%,andtheincidenceofECGabnor-malitiesinhemorrhagicstrokepatientswas79.
23%,confirmingahighincidenceofstroketionrate(46.
15%)amongECGabnormalities;thehighlyimproveddetectionrateduringrecov-erysuggeststhatECGabnormalitiesinstrokepatientsarereversibleandcanbebacktonor-malgraduallythroughtreatment.
Inlinewithourstudy,Sudhishetal.
alsoreportedthatpatientswithacuteischemicstrokeshowedasignificantST-Tdepressionwithgradualrecov-ery[18].
Astoarrhythmia,severearrhythmia,especiallytorsadesdepointes,causedbyneu-rogenicstrokemightleadtodeath.
Thismaybebecauseparasympatheticregulationwaseasilyaffectedbycerebralfunctionalimpairment,thuscausingarrhythmia,orcardiovasculardys-functionresultingfromintracranialhemorrhageledtocardiacdamage.
Therefore,it'sessentialtomonitorPwaveandheartrhythmduringrecovery,withparticularfocusontheoccur-Table5.
ComparisonofincidencesofECGabnormalitiesbe-tweentheacuteandrecoveryphaseinCHgroup(n,%)ECGabnormalitiesAcutephaseRecoveryphaseχ2PPwaveabnormalities69(53.
08%)55(42.
31%)3.
0220.
082ST-Tdepression59(45.
38%)33(25.
38%)11.
3720.
001Arrhythmia58(44.
62%)47(36.
15%)1.
9330.
164Qwaveabnormalities4(3.
08%)3(2.
31%)0.
1470.
702QTintervalprolongation5(3.
85%)3(2.
31%)0.
1290.
720SignificantUwave4(3.
08%)2(1.
54%)0.
1710.
680Note:CH:cerebralhemorrhage;ECG:electrocardiographic.
Table6.
ComparisonofincidencesofECGabnormalitiesbe-tweentheacuteandrecoveryphaseinCIgroup(n,%)ECGabnormalitiesAcutephaseRecoveryphaseχ2PPwaveabnormalities47(36.
15%)33(25.
38%)3.
5390.
060ST-Tdepression61(46.
92%)37(28.
46%)9.
4330.
002Arrhythmia42(32.
31%)27(20.
77%)4.
4390.
035Qwaveabnormalities4(3.
08%)1(0.
77%)0.
8160.
366QTintervalprolongation4(3.
08%)2(1.
54%)0.
1710.
680SignificantUwave2(1.
54%)0(0%)0.
5040.
478Note:CI:cerebralischemia;ECG:electrocardiographic.
Table7.
Comparisonofcardiovasculardiseaseincidence(n,%)GroupCasesofECGabnormalitiesintheacutephaseCasesofCHDaftertreatmentχ2PCIgroup8928(31.
46%)4.
9170.
027CHgroup10344(42.
72%)Note:CI:cerebralischemia;CH:cerebralhemorrhage;ECG:electrocardiographic;CHD:coronaryheartdisease.
combinedwithcardiacdiseas-es.
Moreover,previousstudiesofECGchangesinstrokepatientshaveunveiledthatECGchangesareassociatedwithstrokelocationandrecov-erystatus,andstrokepatientsweremorelikelytodevelopcar-diacsequelae,e.
g.
,thosewithPwaveabnormalitiesandsignifi-cantST-Tdepressionintheacutephasehaveahighrateofcardiovascularsequelae[16,17].
Inthisstudy,ECGchangeswe-reanalyzedinpatientswithacutestrokeandtheabnormalwaveformsmainlyconsistedofPwaveabnormalities,ST-Tde-pressionandarrhythmia.
AstoPwaveabnormalities,itmainlyreferredtohighamplitudePwave,whoseincidencerateinhemorrhagestrokepatientswasupto53.
08%.
Intherecov-eryphase(2weeksaftertreat-ment),Pwaveamplitudegradu-allydecreased,whilenosignifi-cantdifferencewasfoundbe-tweenPwaveabnormalitiesintheacuteandrecoveryphase,indicatingthatalongerobser-vationtimemaybeneeded.
AstoST-Tdepression,theresultsdemonstratedaflatorinvertedTwaveandthehighestdetec-ECGchangesinacutestrokepatients7792IntJClinExpMed2020;13(10):7787-7793renceofcardiovasculardiseases.
Inthisstudy,weshowedthattheincidencesofPwaveabnor-malitiesandarrhythmiawerehigherintheCHgroupthantheCIgroupintherecoveryphase,whilenosignificantchangewasobservedbetweentheincidencesduringtheacuteandrecoveryphase.
Furthermore,thisstudydem-onstratedmarkedlyhigherincidencesofCHDandautonomicdysfunctionintheCHgroupthantheCIgroup.
Thismaybebecausehypo-thalamicinjuryresultingfromhemorrhagestrokeledtoactivationofthesympathetic-adrenalsystem.
Hence,wespeculatedthattheECGchangesmaybeoneoftheauxiliaryindica-torsforassessingtherehabilitationstatusofpatientsandtheriskofsequelae.
Currently,thespecificcausesandmechanismsofECGchangesinacutestrokepatientsarestillnotveryclear.
Somephysicianscientistsbelievethatitmayberelatedtothestructureofdiencephalonandbrainstem[19,20].
ThechangesinreleaseofmediatorscausedbyalterationsofsympatheticandvagalnervoustensionresultedinECGabnormalities.
Forexample,theanteriorcranialfossamaycauseECGchanges,andcerebellartonsillardamagemaycauseinfarct-likeECGchanges[21].
Severallimitationsstillremaininthisstudythoughwehaveachievedcertainpositiveresults.
Thediseasetypeswerenotvarious,andthemonitoringtimewaslimitedintherecoveryphase,somorestudiesareneededtogetamorepreciseconclusioninthefuture.
Insummary,wereportahighincidenceofECGabnormalitiesinacuteneurogenicpatients,andareducedabnormalityrateinmostpatientsduringrecoveryaftertreatment.
CHpatientsshowahigherincidenceofabnormalitiesthanCIpatients,andCHpatientswithPwaveabnor-malitiesandsignificantST-Tdepressionintheacutephaseshowacomparativelyhighinci-denceofcardiovascularsequelae.
Hence,ECGmonitoringhascertainclinicalsignificanceforclinicalobservationandprognosisinpatientswithacuteneurogenicstroke.
DisclosureofconflictofinterestNone.
Addresscorrespondenceto:YuechunShen,De-partmentofCardiovasology,TheFirstAffiliatedHospitalofGuangzhouMedicalUniversity,No.
151YanjiangWestRoad,Guangzhou510120,Guang-dongProvince,China.
Tel:+86-020-83063091;E-mail:shenyuechung1ya@163.
comReferences[1]LiuJ,ZhengL,ChengY,ZhangS,WuB,WangD,ZhangS,TaoW,WuSandLiuM.
Trendsinoutcomesofpatientswithischemicstroketreatedbetween2002and2016:insightsfromaChinesecohort.
CircCardiovascQualOutcomes2019;12:e005610.
[2]FeiginVL,KrishnamurthiRV,ParmarP,Norrv-ingB,MensahGA,BennettDA,Barker-ColloS,MoranAE,SaccoRL,TruelsenT,DavisS,Pan-dianJD,NaghaviM,ForouzanfarMH,NguyenG,JohnsonCO,VosT,MeretojaA,MurrayCJandRothGA.
Updateontheglobalburdenofischemicandhemorrhagicstrokein1990-2013:theGBD2013study.
Neuroepidemiolo-gy2015;45:161-176.
[3]GuoX,LiZ,ZhouY,YuS,YangH,ZhengL,LiuYandSunY.
MetabolicprofileforpredictionofischemicstrokeinChinesehypertensivepopu-lation.
JStrokeCerebrovascDis2019;28:1062-1069.
[4]LiuM,WuB,WangWZ,LeeLM,ZhangSHandKongLZ.
StrokeinChina:epidemiology,pre-vention,andmanagementstrategies.
LancetNeurol2007;6:456-464.
[5]KongJ,XieLX,LiuPL,JingM,HUWHandZhangSQ.
Effectsofaspirinandclopidogrelontheriskofuppergastrointestinalbleedinginpatientswithcardiovascularandcerebrovas-culardiseases.
ZhongguoShengHuaYaoWuZaZhi2017;37:153-155.
[6]ShenM,NiuXandWangL.
Applicationofbloodlipidlevelmonitoringindiagnosisandtherapyofcardiovascularandcerebrovasculardiseases.
ZhonghuaJianYanYiXueZaZhi2018;41:893-896.
[7]FreedmanB,SchnabelRandCalkinsH.
Op-portunisticelectrocardiogramscreeningforatrialfibrillationtopreventstroke.
JAMACardi-ol2019;4:91-92.
[8]BobingerT,KallmunzerB,KoppM,KurkaN,ArnoldM,HeiderS,SchwabSandKohrmannM.
DiagnosticvalueofprehospitalECGinacutestrokepatients.
Neurology2017;88:1894-1898.
[9]WenZJ,WuC,ShenMF,MeiBBandDingJP.
Therelationshipbetweenstrokelocationandpost-strokedepressioninfirst-everstrokepa-tients:ameta-analysis.
ChongqingMed2017;46:2677-2682.
[10]CerasuoloJO,CiprianoLEandSposatoLA.
Thecomplexityofatrialfibrillationnewlydiagnosedafterischemicstrokeandtransientischemicattack:advancesanduncertainties.
CurrOpinNeurol2017;30:28-37.
ECGchangesinacutestrokepatients7793IntJClinExpMed2020;13(10):7787-7793[11]FengX,LiY,WangY,LiL,LittlePJ,XuSWandLiuS.
Danhonginjectionincardiovascularandcerebrovasculardiseases:pharmacologicalactions,molecularmechanisms,andthera-peuticpotential.
PharmacolRes2019;139:62-75.
[12]GuHQ,RaoZZ,YangX,WangCJ,ZhaoXQ,WangYL,LiuLP,WangCY,LiuC,LiH,LiZX,XiaoRPandWangYJ.
Useofemergencymedi-calservicesandtimelytreatmentamongisch-emicstroke.
Stroke2019;50:1013-1016.
[13]SilsbyM,DumaSR,FoisAF,YinYWK,KoryznaJ,MahantN,EvansAandFungVSC.
Timetoacutestroketreatmentin-hourswasmorethanhalvedaftertheintroductionoftheHel-sinkiModelatWestmeadHospital.
InternMedJ2019;49:1386-1392.
[14]RuthiragoD,JulayanontP,TantrachotiP,KimJandNugentK.
Cardiacarrhythmiasandabnor-malelectrocardiogramsafteracutestroke.
AmJMedSci2016;351:112-118.
[15]StoneJ,Mor-AviV,ArdeltAandLangRM.
Fre-quencyofinvertedelectrocardiographictwaves(cerebraltwaves)inpatientswithacutestrokesandtheirrelationtoleftventricularwallmotionabnormalities.
AmJCardiol2018;121:120-124.
[16]KumarS,SharmaGDandDograVD.
Astudyofelectrocardiogramchangesinpatientswithacutestroke.
IntJResMedSci2016;4:2930-2937.
[17]HsiehCY,LinHJ,HuYHandSungSF.
Strokeseveritymaypredictcausesofreadmissionwithinoneyearinpatientswithfirstischemicstrokeevent.
JNeurolSci2017;372:21-27.
[18]SudhishG,MoorthySandMadhavanK.
Astudyofelectrocardiographicabnormalitiesinpatientswithacutecerebrovascularevents.
JClinDiagnRes2019;13:13-16[19]Martin-GallegoA,Gonzalez-GarciaL,Carrasco-BrenesA,Segura-Fernandez-NoguerasM,Delgado-BabianoA,Ros-SanjuanA,Romero-MorenoL,Dominguez-PaezM,Dawid-MilnerMSandArraez-SanchezMA.
Brainstemandautonomicnervoussystemdysfunction:aneu-rosurgicalpointofview.
ActaNeurochirSuppl2017;124:221-229.
[20]OkunlolaAI,OlowoyoP,OkunlolaCKandBaba-lolaOF.
Posteriorcirculationstrokemimickingapontomedullarybrainstemlesion:acasere-port.
InterdiscipNeurosurg2019;18:100491.
[21]KatsanosAH,KorantzopoulosP,TsivgoulisG,KyritsisAP,KosmidouMandGiannopoulosS.
Electrocardiographicabnormalitiesandcardi-acarrhythmiasinstructuralbrainlesions.
IntJCardiol2013;167:328-334.
- parasympathetic7788k.com相关文档
- orange7788k.com
- 氯仿7788k.com
- Companies7788k.com
- clocker7788k.com
- 苯基7788k.com
- 生物多样性7788k.com
Friendhosting,美国迈阿密机房新上线,全场45折特价优惠,100Mbps带宽不限流量,美国/荷兰/波兰/乌兰克/瑞士等可选,7.18欧元/半年
近日Friendhosting发布了最新的消息,新上线了美国迈阿密的云产品,之前的夏季优惠活动还在进行中,全场一次性45折优惠,最高可购买半年,超过半年优惠力度就不高了,Friendhosting商家的优势就是100Mbps带宽不限流量,有需要的朋友可以尝试一下。Friendhosting怎么样?Friendhosting服务器好不好?Friendhosting服务器值不值得购买?Friendho...
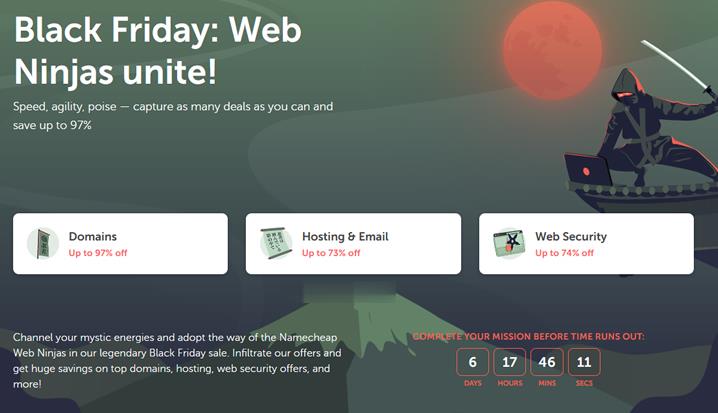
NameCheap黑色星期五和网络礼拜一
如果我们较早关注NameCheap商家的朋友应该记得前几年商家黑色星期五和网络星期一的时候大促采用的闪购活动,每一个小时轮番变化一次促销活动而且限量的。那时候会导致拥挤官网打不开迟缓的问题。从去年开始,包括今年,NameCheap商家比较直接的告诉你黑色星期五和网络星期一为期6天的活动。没有给你限量的活动,只有限时六天,这个是到11月29日。如果我们有需要新注册、转入域名的可以参加,优惠力度还是比...
青果云(590元/年),美国vps洛杉矶CN2 GIA主机测评 1核1G 10M
青果网络QG.NET定位为高效多云管理服务商,已拥有工信部颁发的全网云计算/CDN/IDC/ISP/IP-VPN等多项资质,是CNNIC/APNIC联盟的成员之一,2019年荣获国家高薪技术企业、福建省省级高新技术企业双项荣誉。那么青果网络作为国内主流的IDC厂商之一,那么其旗下美国洛杉矶CN2 GIA线路云服务器到底怎么样?官方网站:https://www.qg.net/CPU内存系统盘流量宽带...

7788k.com为你推荐
-
特朗普取消访问丹麦特朗普首次出访为什么选择梵蒂冈seo优化工具SEO优化要用到什么软件?www.javmoo.comjavimdb是什么网站为什么打不开www.mywife.ccmywife哪部最经典www.bbb551.com广州欢乐在线551要收费吗?33tutu.com33gan.com改成什么了百度关键字百度推广多少关键词合适云鹏清动如脱兔 静若处子 怎么解释长房娇人物描写片段,不用太长,150字左右,要有出处!急!!!!!窝尚公寓蜗尚公寓是个什么网?蜗尚公寓到底是做什么的?