groupstudentmain
studentmain 时间:2021-01-12 阅读:()
Proceedingsofthe3rdInternationalConferenceonComputingandInformatics,ICOCI2011,8-9June,2011Bandung,IndonesiaPaperNo.
021226ANIMPROVEDALGORITHMINTESTCASEGENERATIONFROMUMLACTIVITYDIAGRAMUSINGACTIVITYPATHNorLailyHashim1,YasirD.
Salman21UniversitiUtaraMalaysia,Malaysia,laily@uum.
edu.
my2UniversitiUtaraMalaysia,Malaysia,s820400@uum.
edu.
myABSTRACT.
ThispaperproposedanimprovedalgorithmtoautomaticallygeneratetestcasesdirectlyfromUMLactivitydiagramusinganactivitygraph.
ThisalgorithmhasbeenimplementedasaprototypeusingUMLactivitydiagramsasinputstogeneratetestcases.
Thesegeneratedtestcasesaregeneratedautomaticallyarecomparedtotestcasesthataregeneratedmanuallyinordertoevaluatethealgorithm'susabilityandreliability.
Theresultshowsthatthetestcasesgeneratedbythedevelopedtestcasegeneratorprogramarethesameastheonemanuallyderived.
Keywords:testcasegeneration,automatedgeneration,testcaseINTRODUCTIONTestcasegenerationisoneofthemostimportantelementsforthetestingeffortsforprogramsandapplications(Linzhangetal.
,2004).
Itisespeciallycomplicatedwhenasystemcontainssimultaneouslyexecutingparticipants,sinceasystemlikethatcanshowdifferentresponsesdependingonthesimultaneousoccurrenceconditions.
AUnifiedModellingLanguage(UML)activitydiagramisasuitablemodellinglanguagefordescribinginteractionsbetweensystemobjectsgiventhatanactivitydiagramcanbeconvenientlyusedtocapturebusinessprocesses,workflowsandinteractionscenarios(Kimetal.
,2007).
ManyhavegeneratedtestcasesfromUMLactivitydiagramsbygeneratingthemmanuallytotestthesystem(Linzhangetal.
,2004;Kundu&Samanta,2009;Kimetal.
,2007).
Manygeneratetestcasesautomaticallyusingdifferentmethods(Chenetal.
,2009;Javed,Strooper&Watson,2009),howevernoneofthesestudieshasrevealedthealgorithmthattheyhaveused.
Kundu&Samanth(2009)havedevelopedanalgorithmtogeneratetestcasesusingactivitypaths.
Theiralgorithmhasneverbeenimplementedandthisalgorithmneedsanactivitygraphthathasbeengeneratedmanuallyfromtheactivitydiagram.
Theiralgorithmalsoneedstoenterthetypeofeachnodemanuallyandapplysomerulestogettheresultpaths.
ThispaperfocusesonextendingKundu&Samanth(2009)'salgorithmusedingeneratingtestcasesusingUMLactivitydiagrambyapplyingactivitypathapproach,inwhichthetestcasesaregeneratedautomaticallygenerated.
Theactivitypathisamethodtocalculateallpossiblepathsfromtheactivitydiagrams,convertedeachnumberinthepathtoitsoriginaldata,andfromtherewillgeneratethetestcases.
Proceedingsofthe3rdInternationalConferenceonComputingandInformatics,ICOCI2011,8-9June,2011Bandung,IndonesiaPaperNo.
021227BACKGROUNDThefollowingarethemainconceptsappliedinthisstudy.
UMLActivityDiagramUMLisastandardthatcontainsalargesetofmodellingconceptsthatarerelatedincomplexways.
SinceUMLbecameastandardofOMGin1997,UMLmodelshavebecomemainclassofartefactsinsoftwaredevelopmentprocesses.
UMLprovidesanumberofdiagramstodescribedifferentaspectsofsoftwareartefacts.
UMLactivitydiagramsillustratethesequentialcontrolflowsofactivities.
Theycanbeusedtorepresentcontrolflowofanoperationormodelthedynamicaspectsofagroupofobjects,whichformakindofdesignspecificationsforprograms(Chenatal.
,2009).
Inordertodirectlyreusetheactivitydiagramsmodelingofanoperationasatestmodeltogeneratetestcases,itisnecessarytofollowthetestabilityrequirement.
Anactivitydiagramshouldonlyhaveoneinitialactivitystate,pairofbranchesandmerges,pairofforksandjoins.
Theownerobjectofeachactivitystateshouldbelabeledbyswimlanes,orbelabeledinthenameofactivitystate.
Everynodeotherthantheinitialnodeandfinalnodehasatleastoneoutgoingedgeandoneincomingedge,whichmeansallnodesarereachable.
Anyforknodeonlyhastwoexitedges.
Concurrentactivitystateswillnotaccessthesameobjectandonlyexecuteasynchronously(Linzhangetal.
,2004).
ActivitygraphAnactivitygraphisadirectedgraphwhileitsconstructisrepresentedbyeachnodeintheactivitygraph(initialnode,decisionnode,flowfinalnode,guardcondition,joinnode,forknode,etc.
),andfromthateachborderoftheactivitygraphsymbolizesthestreamintheactivitydiagram.
Furthermore,theactivitygraphasshowninFigure1summarizesassembleofanactivitydiagraminanorganizedwaywhichcanbeusedforfurtherautomation(Kundu&Samanta,2009).
Thesenodesareusedfortestcasegenerationduetotheircapabilityfordetectingmorefaultsinthesynchronizationandloopfaultsthantheotherapproaches.
Inadditiontheabilitytoidentifylocationofthefaultswillhelptoreducetestingaffordandhavingmodel-basedtestcasegenerationtoimproveanddevelopdesignquality.
Furthermore,ithasapossibilitytobuiltautomaticallyprototypefortheactivitygraph.
ThealgorithmbyKundu&Samanta(2009)hastakentheactivitygraphasaninputandtheoutputfromitwillbetheactivitypath.
Furthermore,thegeneratedpathswillneedsomeofrulestoapplyontheresultpathstogetallthepossiblepathsthatwillbeneededtogeneratethetestcases.
Figure1.
ActivityGraphforloginscreenProceedingsofthe3rdInternationalConferenceonComputingandInformatics,ICOCI2011,8-9June,2011Bandung,IndonesiaPaperNo.
021228TestCaseGenerationTestcasegenerationhasattractedmoreandmoreresearchattention(Cartaxo,Neto&Machado,2007;Chenatal.
,2009;Heumann,2001;Javed,Strooper,&Watson,2007;Kimetal.
,2007;Kundu&Samanta,2009;Linzhangatal.
,2004;Mingsong,Xiaokang,&Xuandong,2006).
LargenumberofthemfocusedonUMLactivitydiagramasabasedtogeneratethetestcase(Chen,atal,2009;Kundu&Samanta,2009;Kim,Kang,Baik,&Ko,2007;Linzhangatal.
,2004;Mingsong,Xiaokang,&Xuandong,2006),andnoneofthemrevealtheirproposedapproachesoralgorithms,orsharetheirtestingimplementationconductedduringthetesting.
Atestcasespecifiesasetoftestinputs,expectedresults,andexecutionconditionsdevelopedtoverifyobservancewithaspecificrequirementorimplementaparticularprogrampath(Lilly&G,2010).
PROPOSEDALGORITHMFORGENERATINGTESTCASESThefollowingalgorithmwillgenerateallthepossiblepathsfromtheactivitydiagram,andfromtheresultpaths,testcaseswillbegenerated.
Thisalgorithmisevaluatedintermsofitsusabilityandreliabilitybycomparingmanualtestcaseswithtestcasesautomaticallygeneratedfromtheprototypeofthisalgorithm.
ThemanualtestcasesareobtainedfromAlshammari(2010),wherefourtestcasesforstudentfunctionalitiesfromUniversitiUtaraMalaysialearningmanagementsystemcalled,LearningZoneareused.
Thefunctionsarelogin,downloadassignment,changepassword,andforumsearch.
Duetospacelimitation,onlyoneLoginfunctionisusedandpresentedinthispaper.
Algorithm1:GenerateTestCasePartA:variablesusedintheAlgorithmInput:anactivitydiagramOutput:testcaseTofindthenumberofpaths,thefollowingarethevariablesused:TDN-thenumberofnodewhichhastwodirections.
RNN-thenumberofreturnnode.
TDNI-thenumberoftwodirectionsinsideeachreturnnode.
RNNI-thenumberofreturnnodeinsideeachreturnnode.
Basicpathswiththereturnpathsnumber(BPR)=TDN+1Basicpathsnumber(BP)=BPR-RNNNumberofpathsafterreturn(PAR)=TDNI-RNNIThenumberofallpaths(AP)=BP+PAR(s)PartB:Pseudocodeofmethodssupportedinthealgorithm1.
Tofindthebasicpathswiththereturnpaths,thefollowingarethevariablesused:a.
Node-toputthenodesb.
LoopFlag-tokeeptrackoftheloopc.
N1-forthefirstnextofthenodesd.
N2-forthesecondnextofthenodese.
Nodeflag–forkeepingtrackofthevisitednodesf.
End–forknowtheendofthepathBeginLoopFlag=TDN,Node=firstnode,Nodeflag=0,End=trueWhileLoopFlagisnotemptydoWhileEndistruedoProceedingsofthe3rdInternationalConferenceonComputingandInformatics,ICOCI2011,8-9June,2011Bandung,IndonesiaPaperNo.
021229If(it'sthefirstnode)thenputthefirstnodeinthepath;PutthenodefirstnextinN1anditssecondnextinN2;If(N1=0)thenputendtotrue;If(NodeFlag=0andN2=0)thenputN1forthenextnodeinthepath;Elseif(NodeFlag=0andN2!
=0)thenputN1forthenextnodeinthepathandputNodeFlag=1,putNodeFlag=NodeFlag–thenumberoftwodirectionnodebeforeit;Elseif(NodeFlag=1andN2!
=0)thenputN2forthenextnodeinthepathandputNodeFlag=2;Putthenextnodeofthepathasthecurrentnode;EndPutthepathinarray;End2.
Tofoundallthepaths(AP)DuplicatethepathsthathavewithoutEndtothe(TDNI+RNNI)number;Putthereturnpathsinsideittocontinueittothenumberofpathsinsidethereturnpath;Finisheachonefromthesizebasicpaths;Thatwillgeneratethepossiblepaths.
3.
Fromthesaveinformationofeachnode,printoutthedetailsofeachpathtothelastone,whatwillgiveusthetestcase.
AutomaticgenerateforthetestcasefromtheloginactivitydiagramFirst:Usetheactivitydiagram,asshowninFigure2togeneratethetestcasefromit.
Figure2.
ActivityDiagramfor"Login"Usingthealgorithmexplainedearlier,theprototypewillgeneratethefollowingresultasshowninFigure3No.
ofTimes>N>Y>>Proceedingsofthe3rdInternationalConferenceonComputingandInformatics,ICOCI2011,8-9June,2011Bandung,IndonesiaPaperNo.
021230Figure3.
Theprogramresultforthe"login"activitydiagramThisresultcontainsallpossiblepathsthataregeneratedfromthealgorithmbasedongivenactivitydiagramasshowninFigure3.
Thedetailforeachpathtogetherwithsavednodesisusedtogeneratethetestcases.
ThetestcasesgeneratedforLoginactivitydiagramcanbeseeninTable1inthelastcolumn.
Columntwoshowsthebranchconditionsthateachpathfollows.
Table1.
Thegeneratedtestcasesfor"Login"TestcaseSequenceofBranchConditionsActivitySequence1RegID=InvalidTryagain=NoDisplay:Loginhereusingyourusernameandpassword,Display:Sorry,youhaveexceededtheallowednumberofloginattempts.
Restartyourbrowser.
2RegID=ValidDisplay:Loginhereusingyourusernameandpassword,Launchstudentmainviewpage.
3RegID=InvalidTryagain=YesRegID=InvalidTryagain=NoDisplay:Loginhereusingyourusernameandpassword,Display:Invalidlogin,pleasetryagain.
Display:Loginhereusingyourusernameandpassword,Display:Sorry,youhaveexceededtheallowednumberofloginattempts.
Restartyourbrowser.
4RegID=InvalidTryagain=YesRegID=ValidDisplay:Loginhereusingyourusernameandpassword,Display:Invalidlogin,pleasetryagain,Display:Loginhereusingyourusernameandpassword,Launchstudentmainviewpage.
TestResultFourstudentfunctionalitieshavebeenautomaticallygeneratedusingtheproposedtestcasegeneratorprototype.
ThegeneratedtestcasesarecomparedwiththetestcasesmanuallygeneratedbyAlshammari(2010).
Fromthiscomparison,itshowsthatthetestcasesgeneratedTestcasesforeachpathAllpossiblepaths:4pathsarecreatedProceedingsofthe3rdInternationalConferenceonComputingandInformatics,ICOCI2011,8-9June,2011Bandung,IndonesiaPaperNo.
021231bythedevelopedtestcasegeneratorprogramarethesameastheonemanuallyderived.
Therefore,itcanbeconcludedthattheproposedalgorithmisusableandreliable.
FUTUREWORKInthefuture,thisalgorithmcanbegeneralizedsothatitcanaccommodatevarioustestcoveragecriteriawithinthesametestderivationframework.
Thisprototypecanbeimprovedbydevelopingtheabilitytobuilddirectedgraphandparsetestcasesfromit.
TheUMLactivitydiagramsthathavebeenusedinthisresearchwereusingUML1.
0version.
Forthefuturework,theuseofUML2.
0notationisrecommended.
Additionally,theUMLactivitydiagramsweregeneratedmanuallyinthework;therefore,theuseofatoolthatisabletoautomaticallygeneratethesediagramsissuggested.
CONCLUSIONTheuseofactivegraphisagoodmethodtoensurethatthegenerationofthetestcasesautomaticallyusingtheproposedalgorithmanditsimplementation,andusingtheUMLactivitydiagramasabasetoguaranteetheabilityofautomaticimplementation.
Thereusabilityofthisresearchworkcanbeappliedtocompletefullautomaticanalysis.
ThistestwillopennewopportunitytodiscovernewtechniquesormethodsforthetestingusingUMLdiagramsandautomatictestcasesgeneration.
REFERENCESAlshammari,S.
A.
(2010).
GeneratingTestCasesforLearningZone.
Thesis,UUM.
Cartaxo,E.
,Neto,F.
,&Machado,P.
(2007).
TestCaseGenerationbymeansofUMLSequenceDiagramsandLabeledTransitionSystems.
IEEE,1292-1297.
Chen,M.
,Qiu,X.
,Xu,W.
,Wang,L.
,Zhao,J.
,&Li,X.
(2009).
UMLActivityDiagram-BasedAutomaticTestCaseGenerationForJavaPrograms.
TheComputerJournal,52(5),545-556.
Heumann,J.
(2001).
GeneratingTestCasesFromUseCases.
Retrieved5July,2010,from:http://www.
ibm.
com/developerworks/rational/library/content/RationalEdge/jun01/GeneratingTestCasesFromUseCasesJune01.
pdfJaved,A.
,Strooper,P.
,&Watson,G.
(2007).
AutomatedGenerationofTestCasesUsingModel-DrivenArchitecture.
IEEE,3-9.
Kim,H.
,Kang,S.
,Baik,J.
,&Ko,I.
(2007).
TestCasesGenerationfromUMLActivityDiagrams.
IEEE,556-561.
Kundu,D.
,&Samanta,D.
(2009).
ANovelApproachtoGenerateTestCasesfromUMLActivityDiagrams.
JournalofObjectTechnology,8(3),65-83.
Lilly,R.
,&G,U.
(2010).
ReliableMiningofAutomaticallyGeneratedTestCasesfromSoftwareRequirementsSpecification.
InternationalJournalofComputerScienceIssues,87-91.
Linzhang,W.
,Jiesong,Y.
,Xiaofeng,Y.
,Jun,H.
,Xuandong,L.
,&Guoliang,Z.
(2004).
GeneratingTestCasesfromUMLActivityDiagrambasedonGray-BoxMethod.
IEEE,284-291.
Mingsong,C.
,Xiaokang,Q.
,&Xuandong,L.
(2006).
AutomaticTestCaseGenerationforUMLActivityDiagrams.
ACM,2-8.
021226ANIMPROVEDALGORITHMINTESTCASEGENERATIONFROMUMLACTIVITYDIAGRAMUSINGACTIVITYPATHNorLailyHashim1,YasirD.
Salman21UniversitiUtaraMalaysia,Malaysia,laily@uum.
edu.
my2UniversitiUtaraMalaysia,Malaysia,s820400@uum.
edu.
myABSTRACT.
ThispaperproposedanimprovedalgorithmtoautomaticallygeneratetestcasesdirectlyfromUMLactivitydiagramusinganactivitygraph.
ThisalgorithmhasbeenimplementedasaprototypeusingUMLactivitydiagramsasinputstogeneratetestcases.
Thesegeneratedtestcasesaregeneratedautomaticallyarecomparedtotestcasesthataregeneratedmanuallyinordertoevaluatethealgorithm'susabilityandreliability.
Theresultshowsthatthetestcasesgeneratedbythedevelopedtestcasegeneratorprogramarethesameastheonemanuallyderived.
Keywords:testcasegeneration,automatedgeneration,testcaseINTRODUCTIONTestcasegenerationisoneofthemostimportantelementsforthetestingeffortsforprogramsandapplications(Linzhangetal.
,2004).
Itisespeciallycomplicatedwhenasystemcontainssimultaneouslyexecutingparticipants,sinceasystemlikethatcanshowdifferentresponsesdependingonthesimultaneousoccurrenceconditions.
AUnifiedModellingLanguage(UML)activitydiagramisasuitablemodellinglanguagefordescribinginteractionsbetweensystemobjectsgiventhatanactivitydiagramcanbeconvenientlyusedtocapturebusinessprocesses,workflowsandinteractionscenarios(Kimetal.
,2007).
ManyhavegeneratedtestcasesfromUMLactivitydiagramsbygeneratingthemmanuallytotestthesystem(Linzhangetal.
,2004;Kundu&Samanta,2009;Kimetal.
,2007).
Manygeneratetestcasesautomaticallyusingdifferentmethods(Chenetal.
,2009;Javed,Strooper&Watson,2009),howevernoneofthesestudieshasrevealedthealgorithmthattheyhaveused.
Kundu&Samanth(2009)havedevelopedanalgorithmtogeneratetestcasesusingactivitypaths.
Theiralgorithmhasneverbeenimplementedandthisalgorithmneedsanactivitygraphthathasbeengeneratedmanuallyfromtheactivitydiagram.
Theiralgorithmalsoneedstoenterthetypeofeachnodemanuallyandapplysomerulestogettheresultpaths.
ThispaperfocusesonextendingKundu&Samanth(2009)'salgorithmusedingeneratingtestcasesusingUMLactivitydiagrambyapplyingactivitypathapproach,inwhichthetestcasesaregeneratedautomaticallygenerated.
Theactivitypathisamethodtocalculateallpossiblepathsfromtheactivitydiagrams,convertedeachnumberinthepathtoitsoriginaldata,andfromtherewillgeneratethetestcases.
Proceedingsofthe3rdInternationalConferenceonComputingandInformatics,ICOCI2011,8-9June,2011Bandung,IndonesiaPaperNo.
021227BACKGROUNDThefollowingarethemainconceptsappliedinthisstudy.
UMLActivityDiagramUMLisastandardthatcontainsalargesetofmodellingconceptsthatarerelatedincomplexways.
SinceUMLbecameastandardofOMGin1997,UMLmodelshavebecomemainclassofartefactsinsoftwaredevelopmentprocesses.
UMLprovidesanumberofdiagramstodescribedifferentaspectsofsoftwareartefacts.
UMLactivitydiagramsillustratethesequentialcontrolflowsofactivities.
Theycanbeusedtorepresentcontrolflowofanoperationormodelthedynamicaspectsofagroupofobjects,whichformakindofdesignspecificationsforprograms(Chenatal.
,2009).
Inordertodirectlyreusetheactivitydiagramsmodelingofanoperationasatestmodeltogeneratetestcases,itisnecessarytofollowthetestabilityrequirement.
Anactivitydiagramshouldonlyhaveoneinitialactivitystate,pairofbranchesandmerges,pairofforksandjoins.
Theownerobjectofeachactivitystateshouldbelabeledbyswimlanes,orbelabeledinthenameofactivitystate.
Everynodeotherthantheinitialnodeandfinalnodehasatleastoneoutgoingedgeandoneincomingedge,whichmeansallnodesarereachable.
Anyforknodeonlyhastwoexitedges.
Concurrentactivitystateswillnotaccessthesameobjectandonlyexecuteasynchronously(Linzhangetal.
,2004).
ActivitygraphAnactivitygraphisadirectedgraphwhileitsconstructisrepresentedbyeachnodeintheactivitygraph(initialnode,decisionnode,flowfinalnode,guardcondition,joinnode,forknode,etc.
),andfromthateachborderoftheactivitygraphsymbolizesthestreamintheactivitydiagram.
Furthermore,theactivitygraphasshowninFigure1summarizesassembleofanactivitydiagraminanorganizedwaywhichcanbeusedforfurtherautomation(Kundu&Samanta,2009).
Thesenodesareusedfortestcasegenerationduetotheircapabilityfordetectingmorefaultsinthesynchronizationandloopfaultsthantheotherapproaches.
Inadditiontheabilitytoidentifylocationofthefaultswillhelptoreducetestingaffordandhavingmodel-basedtestcasegenerationtoimproveanddevelopdesignquality.
Furthermore,ithasapossibilitytobuiltautomaticallyprototypefortheactivitygraph.
ThealgorithmbyKundu&Samanta(2009)hastakentheactivitygraphasaninputandtheoutputfromitwillbetheactivitypath.
Furthermore,thegeneratedpathswillneedsomeofrulestoapplyontheresultpathstogetallthepossiblepathsthatwillbeneededtogeneratethetestcases.
Figure1.
ActivityGraphforloginscreenProceedingsofthe3rdInternationalConferenceonComputingandInformatics,ICOCI2011,8-9June,2011Bandung,IndonesiaPaperNo.
021228TestCaseGenerationTestcasegenerationhasattractedmoreandmoreresearchattention(Cartaxo,Neto&Machado,2007;Chenatal.
,2009;Heumann,2001;Javed,Strooper,&Watson,2007;Kimetal.
,2007;Kundu&Samanta,2009;Linzhangatal.
,2004;Mingsong,Xiaokang,&Xuandong,2006).
LargenumberofthemfocusedonUMLactivitydiagramasabasedtogeneratethetestcase(Chen,atal,2009;Kundu&Samanta,2009;Kim,Kang,Baik,&Ko,2007;Linzhangatal.
,2004;Mingsong,Xiaokang,&Xuandong,2006),andnoneofthemrevealtheirproposedapproachesoralgorithms,orsharetheirtestingimplementationconductedduringthetesting.
Atestcasespecifiesasetoftestinputs,expectedresults,andexecutionconditionsdevelopedtoverifyobservancewithaspecificrequirementorimplementaparticularprogrampath(Lilly&G,2010).
PROPOSEDALGORITHMFORGENERATINGTESTCASESThefollowingalgorithmwillgenerateallthepossiblepathsfromtheactivitydiagram,andfromtheresultpaths,testcaseswillbegenerated.
Thisalgorithmisevaluatedintermsofitsusabilityandreliabilitybycomparingmanualtestcaseswithtestcasesautomaticallygeneratedfromtheprototypeofthisalgorithm.
ThemanualtestcasesareobtainedfromAlshammari(2010),wherefourtestcasesforstudentfunctionalitiesfromUniversitiUtaraMalaysialearningmanagementsystemcalled,LearningZoneareused.
Thefunctionsarelogin,downloadassignment,changepassword,andforumsearch.
Duetospacelimitation,onlyoneLoginfunctionisusedandpresentedinthispaper.
Algorithm1:GenerateTestCasePartA:variablesusedintheAlgorithmInput:anactivitydiagramOutput:testcaseTofindthenumberofpaths,thefollowingarethevariablesused:TDN-thenumberofnodewhichhastwodirections.
RNN-thenumberofreturnnode.
TDNI-thenumberoftwodirectionsinsideeachreturnnode.
RNNI-thenumberofreturnnodeinsideeachreturnnode.
Basicpathswiththereturnpathsnumber(BPR)=TDN+1Basicpathsnumber(BP)=BPR-RNNNumberofpathsafterreturn(PAR)=TDNI-RNNIThenumberofallpaths(AP)=BP+PAR(s)PartB:Pseudocodeofmethodssupportedinthealgorithm1.
Tofindthebasicpathswiththereturnpaths,thefollowingarethevariablesused:a.
Node-toputthenodesb.
LoopFlag-tokeeptrackoftheloopc.
N1-forthefirstnextofthenodesd.
N2-forthesecondnextofthenodese.
Nodeflag–forkeepingtrackofthevisitednodesf.
End–forknowtheendofthepathBeginLoopFlag=TDN,Node=firstnode,Nodeflag=0,End=trueWhileLoopFlagisnotemptydoWhileEndistruedoProceedingsofthe3rdInternationalConferenceonComputingandInformatics,ICOCI2011,8-9June,2011Bandung,IndonesiaPaperNo.
021229If(it'sthefirstnode)thenputthefirstnodeinthepath;PutthenodefirstnextinN1anditssecondnextinN2;If(N1=0)thenputendtotrue;If(NodeFlag=0andN2=0)thenputN1forthenextnodeinthepath;Elseif(NodeFlag=0andN2!
=0)thenputN1forthenextnodeinthepathandputNodeFlag=1,putNodeFlag=NodeFlag–thenumberoftwodirectionnodebeforeit;Elseif(NodeFlag=1andN2!
=0)thenputN2forthenextnodeinthepathandputNodeFlag=2;Putthenextnodeofthepathasthecurrentnode;EndPutthepathinarray;End2.
Tofoundallthepaths(AP)DuplicatethepathsthathavewithoutEndtothe(TDNI+RNNI)number;Putthereturnpathsinsideittocontinueittothenumberofpathsinsidethereturnpath;Finisheachonefromthesizebasicpaths;Thatwillgeneratethepossiblepaths.
3.
Fromthesaveinformationofeachnode,printoutthedetailsofeachpathtothelastone,whatwillgiveusthetestcase.
AutomaticgenerateforthetestcasefromtheloginactivitydiagramFirst:Usetheactivitydiagram,asshowninFigure2togeneratethetestcasefromit.
Figure2.
ActivityDiagramfor"Login"Usingthealgorithmexplainedearlier,theprototypewillgeneratethefollowingresultasshowninFigure3No.
ofTimes>N>Y>>Proceedingsofthe3rdInternationalConferenceonComputingandInformatics,ICOCI2011,8-9June,2011Bandung,IndonesiaPaperNo.
021230Figure3.
Theprogramresultforthe"login"activitydiagramThisresultcontainsallpossiblepathsthataregeneratedfromthealgorithmbasedongivenactivitydiagramasshowninFigure3.
Thedetailforeachpathtogetherwithsavednodesisusedtogeneratethetestcases.
ThetestcasesgeneratedforLoginactivitydiagramcanbeseeninTable1inthelastcolumn.
Columntwoshowsthebranchconditionsthateachpathfollows.
Table1.
Thegeneratedtestcasesfor"Login"TestcaseSequenceofBranchConditionsActivitySequence1RegID=InvalidTryagain=NoDisplay:Loginhereusingyourusernameandpassword,Display:Sorry,youhaveexceededtheallowednumberofloginattempts.
Restartyourbrowser.
2RegID=ValidDisplay:Loginhereusingyourusernameandpassword,Launchstudentmainviewpage.
3RegID=InvalidTryagain=YesRegID=InvalidTryagain=NoDisplay:Loginhereusingyourusernameandpassword,Display:Invalidlogin,pleasetryagain.
Display:Loginhereusingyourusernameandpassword,Display:Sorry,youhaveexceededtheallowednumberofloginattempts.
Restartyourbrowser.
4RegID=InvalidTryagain=YesRegID=ValidDisplay:Loginhereusingyourusernameandpassword,Display:Invalidlogin,pleasetryagain,Display:Loginhereusingyourusernameandpassword,Launchstudentmainviewpage.
TestResultFourstudentfunctionalitieshavebeenautomaticallygeneratedusingtheproposedtestcasegeneratorprototype.
ThegeneratedtestcasesarecomparedwiththetestcasesmanuallygeneratedbyAlshammari(2010).
Fromthiscomparison,itshowsthatthetestcasesgeneratedTestcasesforeachpathAllpossiblepaths:4pathsarecreatedProceedingsofthe3rdInternationalConferenceonComputingandInformatics,ICOCI2011,8-9June,2011Bandung,IndonesiaPaperNo.
021231bythedevelopedtestcasegeneratorprogramarethesameastheonemanuallyderived.
Therefore,itcanbeconcludedthattheproposedalgorithmisusableandreliable.
FUTUREWORKInthefuture,thisalgorithmcanbegeneralizedsothatitcanaccommodatevarioustestcoveragecriteriawithinthesametestderivationframework.
Thisprototypecanbeimprovedbydevelopingtheabilitytobuilddirectedgraphandparsetestcasesfromit.
TheUMLactivitydiagramsthathavebeenusedinthisresearchwereusingUML1.
0version.
Forthefuturework,theuseofUML2.
0notationisrecommended.
Additionally,theUMLactivitydiagramsweregeneratedmanuallyinthework;therefore,theuseofatoolthatisabletoautomaticallygeneratethesediagramsissuggested.
CONCLUSIONTheuseofactivegraphisagoodmethodtoensurethatthegenerationofthetestcasesautomaticallyusingtheproposedalgorithmanditsimplementation,andusingtheUMLactivitydiagramasabasetoguaranteetheabilityofautomaticimplementation.
Thereusabilityofthisresearchworkcanbeappliedtocompletefullautomaticanalysis.
ThistestwillopennewopportunitytodiscovernewtechniquesormethodsforthetestingusingUMLdiagramsandautomatictestcasesgeneration.
REFERENCESAlshammari,S.
A.
(2010).
GeneratingTestCasesforLearningZone.
Thesis,UUM.
Cartaxo,E.
,Neto,F.
,&Machado,P.
(2007).
TestCaseGenerationbymeansofUMLSequenceDiagramsandLabeledTransitionSystems.
IEEE,1292-1297.
Chen,M.
,Qiu,X.
,Xu,W.
,Wang,L.
,Zhao,J.
,&Li,X.
(2009).
UMLActivityDiagram-BasedAutomaticTestCaseGenerationForJavaPrograms.
TheComputerJournal,52(5),545-556.
Heumann,J.
(2001).
GeneratingTestCasesFromUseCases.
Retrieved5July,2010,from:http://www.
ibm.
com/developerworks/rational/library/content/RationalEdge/jun01/GeneratingTestCasesFromUseCasesJune01.
pdfJaved,A.
,Strooper,P.
,&Watson,G.
(2007).
AutomatedGenerationofTestCasesUsingModel-DrivenArchitecture.
IEEE,3-9.
Kim,H.
,Kang,S.
,Baik,J.
,&Ko,I.
(2007).
TestCasesGenerationfromUMLActivityDiagrams.
IEEE,556-561.
Kundu,D.
,&Samanta,D.
(2009).
ANovelApproachtoGenerateTestCasesfromUMLActivityDiagrams.
JournalofObjectTechnology,8(3),65-83.
Lilly,R.
,&G,U.
(2010).
ReliableMiningofAutomaticallyGeneratedTestCasesfromSoftwareRequirementsSpecification.
InternationalJournalofComputerScienceIssues,87-91.
Linzhang,W.
,Jiesong,Y.
,Xiaofeng,Y.
,Jun,H.
,Xuandong,L.
,&Guoliang,Z.
(2004).
GeneratingTestCasesfromUMLActivityDiagrambasedonGray-BoxMethod.
IEEE,284-291.
Mingsong,C.
,Xiaokang,Q.
,&Xuandong,L.
(2006).
AutomaticTestCaseGenerationforUMLActivityDiagrams.
ACM,2-8.
- groupstudentmain相关文档
- Anastudentmain
- startsstudentmain
- motorstudentmain
- 研究studentmain
- 告警关联技术在EPON网络中的应用
- 打开怎样关闭studentmain
限时新网有提供5+个免费域名
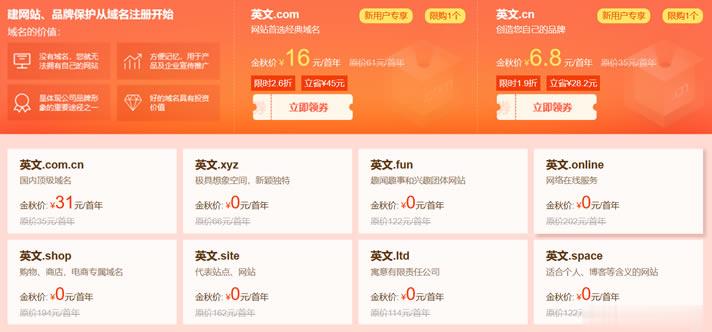
有在六月份的时候也有分享过新网域名注册商发布的域名促销活动(这里)。这不在九月份发布秋季域名促销活动,有提供年付16元的.COM域名,同时还有5个+的特殊后缀的域名是免费的。对于新网服务商是曾经非常老牌的域名注册商,早年也是有在他们家注册域名的。我们可以看到,如果有针对新用户的可以领到16元的.COM域名。包括还有首年免费的.XYZ、.SHOP、Space等等后缀的域名。除了.COM域名之外的其他...
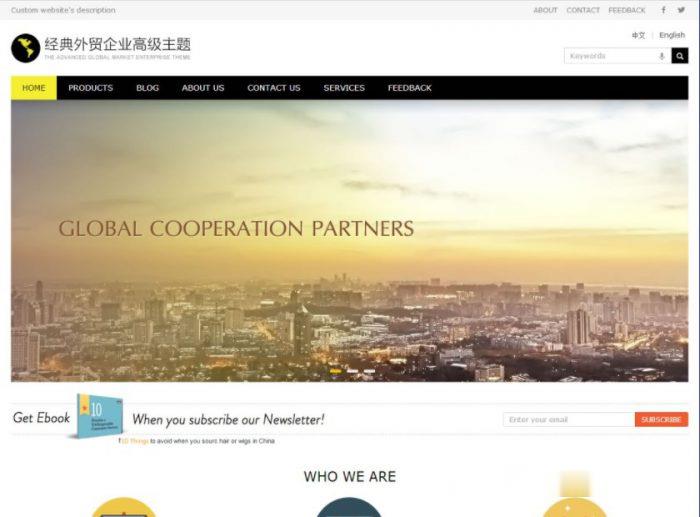
wordpress外贸企业主题 wordpress经典外贸企业建站主题
WordPress经典外贸企业建站主题,经典配色扁平化简约设计+跨屏自适应移动端设备,特色外贸企业建站功能模块+在线Inquiry询单功能,更有利于Google等英文搜索优化和站点收录。采用标准的HTML5+CSS3语言开发,兼容当下的各种主流浏览器: IE 6+(以及类似360、遨游等基于IE内核的)、Firefox、Google Chrome、Safari、Opera等;同时支持移动终端的常用...
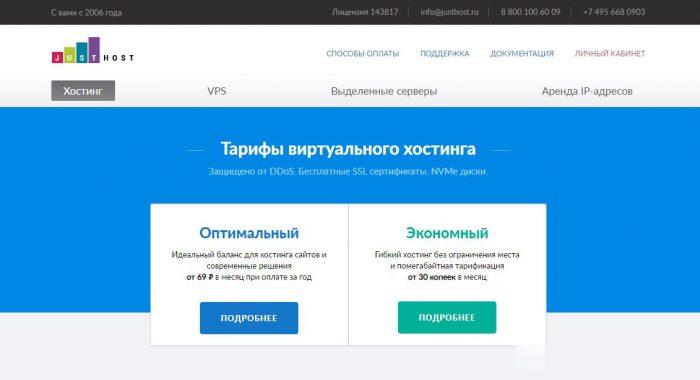
JustHost俄罗斯VPS有HDD、SSD、NVMe SSD,不限流量低至约9.6元/月
justhost怎么样?justhost服务器好不好?JustHost是一家成立于2006年的俄罗斯服务器提供商,支持支付宝付款,服务器价格便宜,200Mbps大带宽不限流量,支持免费更换5次IP,支持控制面板自由切换机房,目前JustHost有俄罗斯6个机房可以自由切换选择,最重要的还是价格真的特别便宜,最低只需要87卢布/月,约8.5元/月起!总体来说,性价比很高,性价比不错,有需要的朋友可以...
studentmain为你推荐
-
虚机虚拟主机是什么东东呢?买虚拟主机购买虚拟主机时,应该注意点什么呢,...?独立ip主机独立IP虚拟主机是什么?有哪些优势?com域名空间我想注册个.com域名和买一个100M空间。com域名空间域名解析,我是一个新手站长,我买了一个空间跟一个COM域名,空间自带一个2级域名,我想把这个COM域名绑定到空间上,咋么办?急急急!求大神帮我,我创建一个游戏论坛,也查不到资料,可以给20元,我的手机13685455534,谢谢查询ip怎么查询IP地址php虚拟空间普通网站需要多大空间?本人新手php学习者,想买个虚拟空间用来放自己做的一些企业站,只是练习用途网站空间价格1M网站空间是多少钱香港虚拟主机推荐一下香港的虚拟主机公司!什么是虚拟主机虚拟主机是什么