area29ff.com
29ff.com 时间:2021-03-20 阅读:()
CopyrightIBMCorporation2001TrademarksWritingasimpleIPv6programPage1of11WritingasimpleIPv6programConfiguringanIPv6addressandportinganIPv4applicationtoIPv6SenthilSundaramSeptember01,2001ThisarticlediscussestheconceptsbehindasimpleIPv6program--specifically,howIPv6solvestheproblemsofaddressspaceandlargeroutingtables.
AprogrammerfamiliarwithIPv4willbeabletorecogniseanIPv6addressandconfigureoneforhismachine.
Thearticlealsocoverstunneling,mappedaddresses,andportingIPv4toIPv6applications,aswellasthelogicofenablinganIPv4clienttohandleIPv6addresses.
Intoday'snetworkingworld,IPv4isthefoundationofnetworking,butinthelast10years,questionshavecomeupdueto:FearofrunningoutofIPv4addressspaceassoonas2002FearofrunningoutofcapacityinglobalroutingtablesNetworkAddressTranslation(NAT)andClasslessInter-DomainRouting(CIDR)(seeRelevantconcepts)havebeenusedasstopgapmeasuresforthesesimplebutseriousproblems.
IPv6--alsocalledIPng(IPnewgeneration)--hasbeenviewedasthelong-termsolution.
ThefollowingenhancementstoIPv4havealsobeenplanned:SimplifiedheaderprocessingSupportforextendedoptionsEnhancementslikequality-of-servicecapabilities,authenticationandprivacycapabilities,flowcontrolcapabilities,andautoconfigurationThekeyrulebehindallthischangeisthatIPv6applicationsshouldcontinuetolivewithIPv4applications.
ThebottomlineisthatIPv6shouldsupportamixedIPv6andIPv4environment.
ThisarticlewillhelpyouquicklyunderstandtheconceptsbehindIPv6andwriteasimpleprograminit.
Let'sstartwithIPv6addressing.
developerWorksibm.
com/developerWorks/WritingasimpleIPv6programPage2of11IPv6addressingTypesofaddressesinIPv6:AnycastisthenewbabyInIPv6,therearethreetypesofaddresses--unicast,multicast,andanycast.
WehadunicastaddressesinIPv4,andmanysystemssupportmulticast,aswell.
AnycastisanewtypeofaddressdefinedbyIPv6.
1.
Unicast:ThisislikeanynormalIPaddressonasingleinterface(forexample,theIPv4address9.
185.
101.
1onen0).
2.
Multicast:Apacketsenttoamulticastaddressisdeliveredtoallinterfacesidentifiedbythataddress.
Thereisnobroadcastaddresstypesincethemulticasttypecantakecareofit.
3.
Anycast:Apacketsenttoananycastaddressisdeliveredtooneoftheinterfacesidentifiedbythataddress(the"nearest"one,accordingtotheroutingprotocols'measureofdistance).
Let'sconsiderasituationwhereanycastaddressescanbeused--connectingtoaserviceprovider'srouter.
Assumethattheserviceprovidercangiveyouasetofaddressestoconnectto,andyouchooseoneoftheseaddresses.
WithIPv6,theserviceprovidercangiveyouananycastaddress,whichyouwillusetoautomaticallyconnecttothe"nearest"address.
ThisisanewfeatureinIPv6andthereisstillalotofdebategoingonaboutitsimplementation.
HowIPv6addressesarewritten:WhatachangeTherearethreeconventionalformsforrepresentingIPv6addressesastextstrings:1.
Theprimaryform:Thepreferredformisx:x:x:x:x:x:x:x,wherethe"x"sarethehexadecimalvalueoftheeight16-bitpiecesoftheaddress.
Twoexamples:fe80:0:0:0:207:30ee:edcb:d05d1080:0:0:0:1:700:200B:417CThereareeighthexfieldsinthefirstaddress:1.
fe802.
03.
04.
05.
2076.
30ee7.
edcb8.
d05dInIPv6,wedonotwritetheleadingzerosinafield.
Thatis,thesecondfieldaboveisjustwrittenas"0"ratherthan"0000.
"Notethatthereare4hexdigitsineachfield.
Eachhexdigitis4bits(andcanrepresentahexvalueof0-F).
Thismeansthatthereare16bitsineachfield(4hexdigitsx4bitsperdigit).
ThetotalsizeofanIPv6addressis128bits(8hexfieldsx16bitsperfield).
2.
Adifferentrepresentationoftheaboveaddress:DuetosomemethodsofallocatingcertainstylesofIPv6addresses,itiscommonforaddressestocontainlongstringsofzerobits.
Inordertomakeiteasiertowriteaddressescontainingzerobits,aspecialsyntaxisavailabletocompressibm.
com/developerWorks/developerWorksWritingasimpleIPv6programPage3of11thezeros.
Theuseof::indicatesmultiplegroupsof16-bitsofzeros.
The::canonlyappearonceinanaddress,andcanalsobeusedtocompresstheleadingzerosinanaddress.
Forexample:FF01:0:0:0:0:0:0:101isamulticastaddressthatcanbewrittenasFF01::101.
0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1isaloopbackaddressthatcanbewrittenas::1.
3.
Fordualenvironments:AnalternativeformthatissometimesmoreconvenientwhendealingwithamixedenvironmentofIPv4andIPv6nodesisx:x:x:x:x:x:d.
d.
d.
d,wherethe"x"sarethehexadecimalvaluesofthesixhigh-order16-bitpiecesoftheaddress,andthe"d"sarethedecimalvaluesofthefourlow-order8-bitpiecesoftheaddress(standardIPv4representation)--thatis,thefirst96bitsarerepresentedas6-x16-bithexfieldsandthelast32bitsare4-x8-bitdecimaldigits.
Forexample:::9.
184.
201.
1::ffff:9.
184.
209.
2IPv6addressprefixTheIPv6addressprefixdenotesthenetworkpartofanaddressandisrepresentedbythenotationipv6-address/prefix-length.
Takethisexample:fe80::206:29ff:fedc:e06e/64Inthisinstance,fe80::206:29ff:fedc:e06eistheaddressand64istheprefixlength.
Thesetwotogethergiveustheaddressprefix.
Intheexample,specifying64meansthatwetakethefirst64bitsoftheabove128-bitaddresstoidentifythenetworkpartoftheaddress.
RelevantconceptsNetworkAddressTranslation(NAT):AnInternetstandardthatenablesalocal-areanetwork(LAN)touseonesetofIPaddressesforinternaltrafficandasecondsetofaddressesforexternaltraffic.
ANATboxlocatedwheretheLANmeetstheInternetmakesallnecessaryIPaddresstranslations.
NATservesthreemainpurposes:ProvidesatypeoffirewallbyhidinginternalIPaddressesEnablesacompanytousemoreinternalIPaddresses;sincethey'reonlyusedinternally,there'snopossibilityofconflictwithIPaddressesusedbyothercompaniesandorganizationsAllowsacompanytocombinemultipleISDNconnectionsintoasingleInternetconnection(SeeRFC1631,"Hide&SeekwithGateways&Translators"inRelatedtopics.
)ClasslessInter-DomainRouting(CIDR):ClasslessInter-DomainRouting.
AnewIPaddressingschemethatreplacestheoldersystembasedonclassesA,B,andC.
WithCIDR,asingleIPaddresscanbeusedtodesignatemanyuniqueIPaddresses.
ACIDRIPaddresslookslikeanormalIPaddressexceptthatitendswithaslashfollowedbyanumber,calledtheIPprefix.
Forexample:172.
200.
0.
0/16TheIPprefixspecifieshowmanyaddressesarecoveredbytheCIDRaddress,withlowernumberscoveringmoreaddresses.
AnIPprefixof/12,forexample,canbeusedtoaddressdeveloperWorksibm.
com/developerWorks/WritingasimpleIPv6programPage4of114,096formerClassCaddresses.
CIDRaddressesreducethesizeofroutingtablesandmakemoreIPaddressesavailablewithinorganizations.
(SeeRelatedtopicsforRFC1517,1518,1519,1520.
)Thisraisesseveralquestions:1.
Howdoestheaboverepresentationsolvethetwoprimaryproblemswearetryingtoaddress:ThefiniteamountofavailableaddressspaceLargeglobalroutingtables2.
HowisthenetworkidentifiedinanIPv4address3.
WhyshouldtheprefixlengthbeallowedtobespecifiedinanIPv6address4.
HowistheprefixspecifiedinanIPv4address5.
WhataretheproblemscausedbythisAndherearetheanswers:Addressspace:Regardingtheaddressspacequestion,RobertMHinden,oneofthekeyfiguresinIPv6efforts,explains:IPV6supportsaddressesthatarefourtimesthenumberofbitsasIPv4addresses(128vs.
32).
Thisis4billiontimes4billiontimes4billion(2^96)timesthesizeoftheIPv4addressspace(2^32).
Thisworksouttobe:340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,607,431,768,211,456Thisisanextremelylargeaddressspace.
Inatheoreticalsensethisisapproximately665,570,793,348,866,943,898,599addressespersquaremeterofthesurfaceoftheplanetEarth(assumingtheearthsurfaceis511,263,971,197,990squaremeters).
Theclassenemy:Nowlet'stakeupthequestionsregardingaddressprefixinIPv4andIPv6.
ThedivisionofIPv4addressspaceintoClassA,B,C,andDnetworkshascausedsomeproblems.
InIPv4,thenetworkpartwasfixedbytheclassoftheaddress.
Let'sillustrateourpointwithanexample.
ClassAaddressescansupport16millionhostsoneachoftheir128networks(becauseinaclassAaddress,thehighest-orderbitissetto0;thenext7bitsareusedforthenetworkpart;andtheremaining24bitsareusedforthelocaladdress).
Now,ifanorganisationweregivenaClassAaddress,anditdidn'thave16millionhosts,thentheremainingaddressspacewouldgotowaste.
AlsonotethateveryonecannotbegivenaClassAaddressasthereareonly127.
CIDRhadtobeintroducedtosolvethisproblemandprolongthelifeofIP.
Thismeansthatthenetworkpartofanaddressshouldnotbefixed.
Thereisaclearneedforanorganisation-specificnetworksize.
Thismeansthatthenetworkpartofanaddressshouldnotbefixed.
ThisvariableprefixlengthisimplementedinIPv6byallowingtheusertospecifythenetworkbitsintheaddressprefix.
Forexample,intheaddressfe80::206:29ff:fedc:e06e/64-,thenumeral64denotesthenetworkpart,andthiscouldbechanged.
Herewehavetheoptionofchoosingthenetworkpart.
Thisisflexible,unlikeIPv4whereithasalwaysbeenfixed.
Routingtables:TheroutesintheInternetgrewintime.
Backbonerouterswereapproachingtheirlimitin1984.
IfCIDRwerenotintroducedtosolvetheproblemofspaceinglobalbackbonerouters,theywouldhavejustcometoahalt.
ibm.
com/developerWorks/developerWorksWritingasimpleIPv6programPage5of11CIDRtechnique:SohowdoesIPv6solvethisproblemThetechniqueforstoppingthisproblemistoallowforaddressprefixesthatfitspecificorganisationalneeds.
ThistechniquewasbasicallyintroducedinCIDR.
InIPv6theprefixorthenetworkpartisalsospecifiedbyauser-specifiednetworkprefix.
ThishelpstoaggregatealargenumberofIPaddressesandspecifyasingleroutefortheorganisation.
Ifanorganisationhasmanynetworks,theninthecaseofIPv4,manynetworkprefixesaretobespecifiedintheglobalroutingtable.
InthecaseofIPv6,wecansimplygiveonehigherlevelroutetorepresentthewholeorganisation,aswecanshrinkandexpandthenetworkprefixbyvaryingit.
Thishelpstheglobaltablestoremainsmall.
ThiskindofsetupdidnotexistinIPv4.
(FormoreonCIDR,refertoRelevantconcepts).
AutoconfigurationinIPv6:PlugandplayWhatisautoconfigurationThefirstthingoneshoulddoistosetupamachinewithanIPv6address.
ThereisaninterestingfeatureinIPv6calledstatelessautoconfigurationthat'sdefinedbyRFC2462(seeRelatedtopics).
ThisRFCstatesthatyourhostshouldbeabletogiveyouanautomatic,globallyuniqueIPv6address.
Forexample,InAIX,yousimplybootupyourmachineandtypeautoconf6-vfromthe#prompt,andyouwillseeyourmachineautomaticallydetectingthesubnetandassigningyouavalidIPngaddress.
IranifconfigtoseetheIPv6address.
Hereisapartialoutputofifconfig-aonmyAIXmachine:inet9.
184.
209.
3netmask0xffffff00broadcast9.
184.
209.
255inet6fe80::207:30ee:edcb:d05d/64Igottheinet6addresswhenIranautoconf-v6(inet6isdefinedonen0).
ThismachinenowhasbothanIPv6andIPv4onthesamephysicalethernetinterface.
HowisthisdoneInverysimpleterms,thelink-layeraddressisusedasabasetogettheIPv6addressandthehostandroutertocommunicate,sothatthehostcangetanideaaboutthesubnet.
(RefertotheRFCforamoredetaileddiscussion.
)HowaboutotheroperatingsystemsTheotherUNIXimplementationshavesimilarIPv6autconfigurationcommandslikeAIX.
Thereisalsoavarietyoffree-softimplementationsofIPv6(seeRelatedtopics).
CanImanuallyconfigureYes.
YoucanalsoconfigureanIPv6addressusingifconfig.
It'simportanttoplanyournetworktoassignthenetworkprefix.
TunnelingandmappedIPngaddresses:ThetransitionshouldbesmoothExampleofatransitionproblemConsiderthissituation.
WehaveanexistingIPv4environmentwithIPv4-onlyhostsandrouters.
Nowlet'ssayweaddafewIPv6routersandhoststoournetwork.
SomeofthesehostshavethecapabilitytohandlebothIPv6andIPv4addresses,andsomeofthemarepureIPv6orpureIPv4.
Ifwehavetowriteanapplicationthatrunsinthisenvironment,thentheapplication'sclientanddeveloperWorksibm.
com/developerWorks/WritingasimpleIPv6programPage6of11servershouldbeabletohandleallpossibleclient-serverpairs.
Thatis,aclientorservercanbepurelyIPv4,purelyIPv6,orbothIPv6-andIPv4-enabled.
(Foradetailedexplanation,readRFC2893:"Transitionmechanismsforhostsandrouters"--seeRelatedtopics.
)WhatisthetunnelingtechniqueAgain,let'stakeanexamplesituation.
WeneedtocarryanIPv6packetoveranIPv4network.
HowdoweproceedSimple--wejustencapsulatetheIPv6packetinanIPv4packetandsenditacrosstheIPv4network.
Thisiscalledtunneling.
Configuredtunneling:WeneedtoconfigurethehostthatisattheentrypointoftheIPv4networksothatitcanconverttheIPv6packetintoanIPv4packet.
Also,thenodethatistheexitpointoftheIPv4networkneedstobeconfiguredsothatitcanconvertthepacketbacktoanIPv6packet.
Thisiscalledconfiguredtunneling.
Automatictunneling:Ifahosthasthecapabilitytodothisconversiondynamicallythenit'scalledautomatictunneling.
SupportforAutomatictunnelingintheprotocol:ThenodesthatutilizethistechniqueareassignedspecialIPv6unicastaddresses.
TheseaddressescarryanIPv4addressinthelow-order32-bits.
ThistypeofaddressistermedanIPv4-compatibleIPv6addressandhasthefollowingformat:|80bits|16|32bits||0000.
0000|0000|IPV4ADDRESS|AsecondtypeofIPv6addressthatholdsanembeddedIPv4addressisalsodefined.
ThisaddressisusedtorepresenttheaddressesofIPv4-onlynodes(thosethatdonotsupportIPv6)asIPv6addresses.
Thistypeofaddressistermedan"IPv4-mappedIPv6address"andhastheformat:|80bits|16|32bits||0000.
0000|FFFF|IPV4ADDRESS|UsageofmappedaddressesIfyouarewritinganIPv6-enabledclient,you'refacedwiththisquestion:DoyousendoutanIPv6packetordoyousendoutanIPv4packetYouaregivennoguaranteeabouttheunderlyingnetwork.
ThenextmachineyoucontacttogetthisconnectioncanbeanIPv6machine,anIPv4machine,oradualhost.
Let'sassumethattheapplicationsresponsibleforroutingtheconnectionsarecapableofknowingwhetherthenextmachineisanIPv6machineoranIPv4machine.
Inthiscase,itwouldbereallyhelpfulifwecouldhaveIPv6addressesthatcancontainIPv4addressesinsidethem.
Itwouldbegoodtohaveamechanism(theffff.
inmappedv4addresses)totellusiftheaddressisreferringtoapureIPv4node;thiswouldhelpusmakeappropriatedecisionsastowhichtypeofpacketistobesent.
Ourdiscussioninthefinalsectionshouldmakethisclearer.
ibm.
com/developerWorks/developerWorksWritingasimpleIPv6programPage7of11PortingIPv4applicationstoIPv6HerearesomethingstoconsiderwhenportinganIPv4applicationtoIPv6:Thesockaddr_in6structureandthein6_addrstructure,whichcanhold128bitaddresses,havebeendefined.
CheckifyouareusingtherelevantIPv6structure.
INADDR_ANYandINADDR_LOOPBACKmustbemodifiedtoin6addr_anyorin6addr_loopbackforassignments.
TheIN6ADDR_ANY_INITorIN6ADDR_LOOPBACK_INITmacroscanbehelpful.
UseAF_INET6insteadofAF_INET.
NotetherearestructuresandprogramsthatwillworkforIPv6andIPv4.
Oneofthelinkspointstoportingexamplesandthislinkcanbereferredto(see"MovingtoIPv6"inRelatedtopics).
NotethatnochangeinthesyntaxisnecessarywhenusingcertainfunctionsforIPv6.
Theonlydifferencewhenusingthesefunctionsisthatyoumustcastsockaddr_in6tostructsockaddr*.
ThefollowingmacrosandfunctionsareusedtowriteIPv6-enabledapplications:TheIN6_IS_ADDR_V4MAPPEDcanbeusedtodeterminewhetheranIPv6addressisanIPv4-mappedaddress.
gethostbynameretrievesanetworkhostentryviaitsnameandaddressfamily.
getaddrinforeturnsaddressinformationrelatedtoaspecifiedservicelocation.
getnameinforeturnsthetextstringsassociatedwiththesuppliedIPaddressandportnumber.
inet_ptonconvertsthespecifiedaddressintextformtoitsbinaryequivalent.
inet_ntopconvertsthespecifiedbinaryaddressintoatextequivalentthat'ssuitableforpresentation.
getaddrinfoandgetnameinfocanbothbeusedtoretrieveinformationrelatedtoIPv4andIPv6addresses.
inet_ptonandinet_ntopcanbothconvertIPv4andIPv6addresses.
Thismeansthatin"IPv6-ready"applications,youdonotneedtouseeitherinet_addrorinet_ntoa.
ThefollowingfunctionsdonotrequireachangeinsyntaxwhenusedforIPv6:bind,connect,sendmsg,sendto,accept,recvfrom,recvmsg,getpeername,andgetsockname,althoughthecodeforthesefunctionshasbeenmodified.
WritingasimpleIPv6clientLet'snowtakealookatthelogicbehindwritinganIPv6-enabledclient.
Ibelieveweareequippedwiththebasics.
WeknowaboutIPv6addresses.
Wewillbeabletorecognisethemifweseethemindifferentrepresentations.
WewillbeabletoautoconfigureanIPv6addressonourmachineusingautoconf.
Wealsoknowaboutthemappedaddresstransitionmechanismandhaveanideaofthefunctionstouse.
ConsiderthefollowingIPv4client:#include#include#include#include#include.
.
.
developerWorksibm.
com/developerWorks/WritingasimpleIPv6programPage8of11main(argc,argv)/*clientside*/intargc;char*argv[];{structsockaddr_inserver;structservent*sp;structhostent*hp;ints;.
.
.
sp=getservbyname("login","tcp");if(sp==NULL){fprintf(stderr,"rlogin:tcp/login:unknownservice\n");exit(1);}hp=gethostbyname(argv[1]);if(hp==NULL){fprintf(stderr,"rlogin:%s:unknownhost\n",argv[1]);exit(2);}memset((char*)&server,0,sizeof(server));memcpy((char*)&server.
sin_addr,hp->h_addr,hp->h_length);server.
sin_len=sizeof(server);server.
sin_family=hp->h_addrtype;server.
sin_port=sp->s_port;s=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);if(s0){//noteinet_ptonwilltakecareofsettingtheaddress.
.
.
.
.
ip6.
sin6_family=AF_INET6;ip6.
sin6_len=sizeof(structsockaddr_in6);.
.
.
.
.
developerWorksibm.
com/developerWorks/WritingasimpleIPv6programPage10of11}else{//nowitsnotav6addressorav4addresssoitshouldbehostname//doav6lookup,notethatav6lookupwilllookforav6addressifnot//presentitcanpickupav4address//resinitisdefinedinresolv.
hres_init();_res.
options|=RES_USE_INET6;hptr=gethostbyname(name);.
.
.
.
.
//checkhptr->h_addrtypeifitsAF_INET6youcancopytheaddressdirectly//ifnotyouneedtomapit.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
if(connect(sd,&ip6,sizeof(ip6<0){//connectfailure.
.
.
.
}else{//continuewiththeprogram.
}SummaryoftheabovelogicTosummarizethelogic,wechecktoseeifwegotadottedIPv4addresstohandle.
Ifso,wegoaheadandmapitandfillinanIPv6structure,tobeusedbytheconnectcalllater.
Ifit'sanIPv6address,wecopyitdirectlytotheIPv6structure.
Ifit'sahostname,wetryanddoanIPv6lookup.
WecangetanIPv4oranIPv6address.
Weknowthisfromthefamilyfield.
Accordingly,weeithermapitorcopyit,thendoasingleconnectcallregardlessofwhetherit'sanIPv4oranIPv6address,andproceedwithourprogram.
ConclusionWehavelookedonlyattheconceptsweneedtowritetheaboveprogram.
Therearemanymoreinterestingconceptsthatwillsoonbecomepartofeverydaylife.
TherearecontroversiesandconstructivedebatesaboutthingslikeDNSforIPv6andstatefulautoconfigurationforIPv6(DHCP).
Thesetopics,alongwithothers,suchasimplementationofotherlayers,howroutingwillbedone,andhowautoconfigurationwillbeimplemented,willmakeforinterestingdiscussion.
IhopetoseeyousooninamoreexcitingIPv6world!
ibm.
com/developerWorks/developerWorksWritingasimpleIPv6programPage11of11RelatedtopicsIPNextGenerationOverview,byRobertMHinden,givesabriefoverviewofalltheIPngconcepts.
KameprojectisajointeffortofsevencompaniesinJapanthatprovideafreeIPv6andIPsec(forbothIPv4andIPv6)stackforBSDvariants.
6boneisanIPv6testbedtoassistintheevolutionanddeploymentofIPv6.
IPv6draftsandRFCscanbefoundinIPngCurrentSpecifications.
Theygivealltherequireddetailsinaclearandlogicalorder.
StatelessautoconfigurationisdefinedinRFC2462:IPv6StatelessAddressAutoconfiguration.
RFC2893,TransitionMechanismsforIPv6HostsandRouters,specifiesIPv4compatibilitymechanismsthatcanbeimplementedbyIPv6hostsandrouters.
AdditionalinformationonNATcanbefoundinRFC1631,TheIPNetworkAddressTranslator(NAT).
Formorein-depthoverviewsofCIDR,readRFC1517,RFC1518,RFC1519,andRFC1520.
FindouthowIPv6forOS/390providesanimplementationofIPv4andIPv6forOS/390.
Planningforgrowth,fromIBM'sHighVolumeWebSiteTeam,canshowyouhowyourWebsitecansatisfyfuturedemandsandevaluatepotentialworkloadandinfrastructurechanges.
IBM'sPatternsfore-businesssitefeaturesanumberofreusableassetsthatcanhelpspeedtheprocessofdevelopingapplications.
BrowsemoreWebarchitectureresourcesondeveloperWorks.
CopyrightIBMCorporation2001(www.
ibm.
com/legal/copytrade.
shtml)Trademarks(www.
ibm.
com/developerworks/ibm/trademarks/)
AprogrammerfamiliarwithIPv4willbeabletorecogniseanIPv6addressandconfigureoneforhismachine.
Thearticlealsocoverstunneling,mappedaddresses,andportingIPv4toIPv6applications,aswellasthelogicofenablinganIPv4clienttohandleIPv6addresses.
Intoday'snetworkingworld,IPv4isthefoundationofnetworking,butinthelast10years,questionshavecomeupdueto:FearofrunningoutofIPv4addressspaceassoonas2002FearofrunningoutofcapacityinglobalroutingtablesNetworkAddressTranslation(NAT)andClasslessInter-DomainRouting(CIDR)(seeRelevantconcepts)havebeenusedasstopgapmeasuresforthesesimplebutseriousproblems.
IPv6--alsocalledIPng(IPnewgeneration)--hasbeenviewedasthelong-termsolution.
ThefollowingenhancementstoIPv4havealsobeenplanned:SimplifiedheaderprocessingSupportforextendedoptionsEnhancementslikequality-of-servicecapabilities,authenticationandprivacycapabilities,flowcontrolcapabilities,andautoconfigurationThekeyrulebehindallthischangeisthatIPv6applicationsshouldcontinuetolivewithIPv4applications.
ThebottomlineisthatIPv6shouldsupportamixedIPv6andIPv4environment.
ThisarticlewillhelpyouquicklyunderstandtheconceptsbehindIPv6andwriteasimpleprograminit.
Let'sstartwithIPv6addressing.
developerWorksibm.
com/developerWorks/WritingasimpleIPv6programPage2of11IPv6addressingTypesofaddressesinIPv6:AnycastisthenewbabyInIPv6,therearethreetypesofaddresses--unicast,multicast,andanycast.
WehadunicastaddressesinIPv4,andmanysystemssupportmulticast,aswell.
AnycastisanewtypeofaddressdefinedbyIPv6.
1.
Unicast:ThisislikeanynormalIPaddressonasingleinterface(forexample,theIPv4address9.
185.
101.
1onen0).
2.
Multicast:Apacketsenttoamulticastaddressisdeliveredtoallinterfacesidentifiedbythataddress.
Thereisnobroadcastaddresstypesincethemulticasttypecantakecareofit.
3.
Anycast:Apacketsenttoananycastaddressisdeliveredtooneoftheinterfacesidentifiedbythataddress(the"nearest"one,accordingtotheroutingprotocols'measureofdistance).
Let'sconsiderasituationwhereanycastaddressescanbeused--connectingtoaserviceprovider'srouter.
Assumethattheserviceprovidercangiveyouasetofaddressestoconnectto,andyouchooseoneoftheseaddresses.
WithIPv6,theserviceprovidercangiveyouananycastaddress,whichyouwillusetoautomaticallyconnecttothe"nearest"address.
ThisisanewfeatureinIPv6andthereisstillalotofdebategoingonaboutitsimplementation.
HowIPv6addressesarewritten:WhatachangeTherearethreeconventionalformsforrepresentingIPv6addressesastextstrings:1.
Theprimaryform:Thepreferredformisx:x:x:x:x:x:x:x,wherethe"x"sarethehexadecimalvalueoftheeight16-bitpiecesoftheaddress.
Twoexamples:fe80:0:0:0:207:30ee:edcb:d05d1080:0:0:0:1:700:200B:417CThereareeighthexfieldsinthefirstaddress:1.
fe802.
03.
04.
05.
2076.
30ee7.
edcb8.
d05dInIPv6,wedonotwritetheleadingzerosinafield.
Thatis,thesecondfieldaboveisjustwrittenas"0"ratherthan"0000.
"Notethatthereare4hexdigitsineachfield.
Eachhexdigitis4bits(andcanrepresentahexvalueof0-F).
Thismeansthatthereare16bitsineachfield(4hexdigitsx4bitsperdigit).
ThetotalsizeofanIPv6addressis128bits(8hexfieldsx16bitsperfield).
2.
Adifferentrepresentationoftheaboveaddress:DuetosomemethodsofallocatingcertainstylesofIPv6addresses,itiscommonforaddressestocontainlongstringsofzerobits.
Inordertomakeiteasiertowriteaddressescontainingzerobits,aspecialsyntaxisavailabletocompressibm.
com/developerWorks/developerWorksWritingasimpleIPv6programPage3of11thezeros.
Theuseof::indicatesmultiplegroupsof16-bitsofzeros.
The::canonlyappearonceinanaddress,andcanalsobeusedtocompresstheleadingzerosinanaddress.
Forexample:FF01:0:0:0:0:0:0:101isamulticastaddressthatcanbewrittenasFF01::101.
0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1isaloopbackaddressthatcanbewrittenas::1.
3.
Fordualenvironments:AnalternativeformthatissometimesmoreconvenientwhendealingwithamixedenvironmentofIPv4andIPv6nodesisx:x:x:x:x:x:d.
d.
d.
d,wherethe"x"sarethehexadecimalvaluesofthesixhigh-order16-bitpiecesoftheaddress,andthe"d"sarethedecimalvaluesofthefourlow-order8-bitpiecesoftheaddress(standardIPv4representation)--thatis,thefirst96bitsarerepresentedas6-x16-bithexfieldsandthelast32bitsare4-x8-bitdecimaldigits.
Forexample:::9.
184.
201.
1::ffff:9.
184.
209.
2IPv6addressprefixTheIPv6addressprefixdenotesthenetworkpartofanaddressandisrepresentedbythenotationipv6-address/prefix-length.
Takethisexample:fe80::206:29ff:fedc:e06e/64Inthisinstance,fe80::206:29ff:fedc:e06eistheaddressand64istheprefixlength.
Thesetwotogethergiveustheaddressprefix.
Intheexample,specifying64meansthatwetakethefirst64bitsoftheabove128-bitaddresstoidentifythenetworkpartoftheaddress.
RelevantconceptsNetworkAddressTranslation(NAT):AnInternetstandardthatenablesalocal-areanetwork(LAN)touseonesetofIPaddressesforinternaltrafficandasecondsetofaddressesforexternaltraffic.
ANATboxlocatedwheretheLANmeetstheInternetmakesallnecessaryIPaddresstranslations.
NATservesthreemainpurposes:ProvidesatypeoffirewallbyhidinginternalIPaddressesEnablesacompanytousemoreinternalIPaddresses;sincethey'reonlyusedinternally,there'snopossibilityofconflictwithIPaddressesusedbyothercompaniesandorganizationsAllowsacompanytocombinemultipleISDNconnectionsintoasingleInternetconnection(SeeRFC1631,"Hide&SeekwithGateways&Translators"inRelatedtopics.
)ClasslessInter-DomainRouting(CIDR):ClasslessInter-DomainRouting.
AnewIPaddressingschemethatreplacestheoldersystembasedonclassesA,B,andC.
WithCIDR,asingleIPaddresscanbeusedtodesignatemanyuniqueIPaddresses.
ACIDRIPaddresslookslikeanormalIPaddressexceptthatitendswithaslashfollowedbyanumber,calledtheIPprefix.
Forexample:172.
200.
0.
0/16TheIPprefixspecifieshowmanyaddressesarecoveredbytheCIDRaddress,withlowernumberscoveringmoreaddresses.
AnIPprefixof/12,forexample,canbeusedtoaddressdeveloperWorksibm.
com/developerWorks/WritingasimpleIPv6programPage4of114,096formerClassCaddresses.
CIDRaddressesreducethesizeofroutingtablesandmakemoreIPaddressesavailablewithinorganizations.
(SeeRelatedtopicsforRFC1517,1518,1519,1520.
)Thisraisesseveralquestions:1.
Howdoestheaboverepresentationsolvethetwoprimaryproblemswearetryingtoaddress:ThefiniteamountofavailableaddressspaceLargeglobalroutingtables2.
HowisthenetworkidentifiedinanIPv4address3.
WhyshouldtheprefixlengthbeallowedtobespecifiedinanIPv6address4.
HowistheprefixspecifiedinanIPv4address5.
WhataretheproblemscausedbythisAndherearetheanswers:Addressspace:Regardingtheaddressspacequestion,RobertMHinden,oneofthekeyfiguresinIPv6efforts,explains:IPV6supportsaddressesthatarefourtimesthenumberofbitsasIPv4addresses(128vs.
32).
Thisis4billiontimes4billiontimes4billion(2^96)timesthesizeoftheIPv4addressspace(2^32).
Thisworksouttobe:340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,607,431,768,211,456Thisisanextremelylargeaddressspace.
Inatheoreticalsensethisisapproximately665,570,793,348,866,943,898,599addressespersquaremeterofthesurfaceoftheplanetEarth(assumingtheearthsurfaceis511,263,971,197,990squaremeters).
Theclassenemy:Nowlet'stakeupthequestionsregardingaddressprefixinIPv4andIPv6.
ThedivisionofIPv4addressspaceintoClassA,B,C,andDnetworkshascausedsomeproblems.
InIPv4,thenetworkpartwasfixedbytheclassoftheaddress.
Let'sillustrateourpointwithanexample.
ClassAaddressescansupport16millionhostsoneachoftheir128networks(becauseinaclassAaddress,thehighest-orderbitissetto0;thenext7bitsareusedforthenetworkpart;andtheremaining24bitsareusedforthelocaladdress).
Now,ifanorganisationweregivenaClassAaddress,anditdidn'thave16millionhosts,thentheremainingaddressspacewouldgotowaste.
AlsonotethateveryonecannotbegivenaClassAaddressasthereareonly127.
CIDRhadtobeintroducedtosolvethisproblemandprolongthelifeofIP.
Thismeansthatthenetworkpartofanaddressshouldnotbefixed.
Thereisaclearneedforanorganisation-specificnetworksize.
Thismeansthatthenetworkpartofanaddressshouldnotbefixed.
ThisvariableprefixlengthisimplementedinIPv6byallowingtheusertospecifythenetworkbitsintheaddressprefix.
Forexample,intheaddressfe80::206:29ff:fedc:e06e/64-,thenumeral64denotesthenetworkpart,andthiscouldbechanged.
Herewehavetheoptionofchoosingthenetworkpart.
Thisisflexible,unlikeIPv4whereithasalwaysbeenfixed.
Routingtables:TheroutesintheInternetgrewintime.
Backbonerouterswereapproachingtheirlimitin1984.
IfCIDRwerenotintroducedtosolvetheproblemofspaceinglobalbackbonerouters,theywouldhavejustcometoahalt.
ibm.
com/developerWorks/developerWorksWritingasimpleIPv6programPage5of11CIDRtechnique:SohowdoesIPv6solvethisproblemThetechniqueforstoppingthisproblemistoallowforaddressprefixesthatfitspecificorganisationalneeds.
ThistechniquewasbasicallyintroducedinCIDR.
InIPv6theprefixorthenetworkpartisalsospecifiedbyauser-specifiednetworkprefix.
ThishelpstoaggregatealargenumberofIPaddressesandspecifyasingleroutefortheorganisation.
Ifanorganisationhasmanynetworks,theninthecaseofIPv4,manynetworkprefixesaretobespecifiedintheglobalroutingtable.
InthecaseofIPv6,wecansimplygiveonehigherlevelroutetorepresentthewholeorganisation,aswecanshrinkandexpandthenetworkprefixbyvaryingit.
Thishelpstheglobaltablestoremainsmall.
ThiskindofsetupdidnotexistinIPv4.
(FormoreonCIDR,refertoRelevantconcepts).
AutoconfigurationinIPv6:PlugandplayWhatisautoconfigurationThefirstthingoneshoulddoistosetupamachinewithanIPv6address.
ThereisaninterestingfeatureinIPv6calledstatelessautoconfigurationthat'sdefinedbyRFC2462(seeRelatedtopics).
ThisRFCstatesthatyourhostshouldbeabletogiveyouanautomatic,globallyuniqueIPv6address.
Forexample,InAIX,yousimplybootupyourmachineandtypeautoconf6-vfromthe#prompt,andyouwillseeyourmachineautomaticallydetectingthesubnetandassigningyouavalidIPngaddress.
IranifconfigtoseetheIPv6address.
Hereisapartialoutputofifconfig-aonmyAIXmachine:inet9.
184.
209.
3netmask0xffffff00broadcast9.
184.
209.
255inet6fe80::207:30ee:edcb:d05d/64Igottheinet6addresswhenIranautoconf-v6(inet6isdefinedonen0).
ThismachinenowhasbothanIPv6andIPv4onthesamephysicalethernetinterface.
HowisthisdoneInverysimpleterms,thelink-layeraddressisusedasabasetogettheIPv6addressandthehostandroutertocommunicate,sothatthehostcangetanideaaboutthesubnet.
(RefertotheRFCforamoredetaileddiscussion.
)HowaboutotheroperatingsystemsTheotherUNIXimplementationshavesimilarIPv6autconfigurationcommandslikeAIX.
Thereisalsoavarietyoffree-softimplementationsofIPv6(seeRelatedtopics).
CanImanuallyconfigureYes.
YoucanalsoconfigureanIPv6addressusingifconfig.
It'simportanttoplanyournetworktoassignthenetworkprefix.
TunnelingandmappedIPngaddresses:ThetransitionshouldbesmoothExampleofatransitionproblemConsiderthissituation.
WehaveanexistingIPv4environmentwithIPv4-onlyhostsandrouters.
Nowlet'ssayweaddafewIPv6routersandhoststoournetwork.
SomeofthesehostshavethecapabilitytohandlebothIPv6andIPv4addresses,andsomeofthemarepureIPv6orpureIPv4.
Ifwehavetowriteanapplicationthatrunsinthisenvironment,thentheapplication'sclientanddeveloperWorksibm.
com/developerWorks/WritingasimpleIPv6programPage6of11servershouldbeabletohandleallpossibleclient-serverpairs.
Thatis,aclientorservercanbepurelyIPv4,purelyIPv6,orbothIPv6-andIPv4-enabled.
(Foradetailedexplanation,readRFC2893:"Transitionmechanismsforhostsandrouters"--seeRelatedtopics.
)WhatisthetunnelingtechniqueAgain,let'stakeanexamplesituation.
WeneedtocarryanIPv6packetoveranIPv4network.
HowdoweproceedSimple--wejustencapsulatetheIPv6packetinanIPv4packetandsenditacrosstheIPv4network.
Thisiscalledtunneling.
Configuredtunneling:WeneedtoconfigurethehostthatisattheentrypointoftheIPv4networksothatitcanconverttheIPv6packetintoanIPv4packet.
Also,thenodethatistheexitpointoftheIPv4networkneedstobeconfiguredsothatitcanconvertthepacketbacktoanIPv6packet.
Thisiscalledconfiguredtunneling.
Automatictunneling:Ifahosthasthecapabilitytodothisconversiondynamicallythenit'scalledautomatictunneling.
SupportforAutomatictunnelingintheprotocol:ThenodesthatutilizethistechniqueareassignedspecialIPv6unicastaddresses.
TheseaddressescarryanIPv4addressinthelow-order32-bits.
ThistypeofaddressistermedanIPv4-compatibleIPv6addressandhasthefollowingformat:|80bits|16|32bits||0000.
0000|0000|IPV4ADDRESS|AsecondtypeofIPv6addressthatholdsanembeddedIPv4addressisalsodefined.
ThisaddressisusedtorepresenttheaddressesofIPv4-onlynodes(thosethatdonotsupportIPv6)asIPv6addresses.
Thistypeofaddressistermedan"IPv4-mappedIPv6address"andhastheformat:|80bits|16|32bits||0000.
0000|FFFF|IPV4ADDRESS|UsageofmappedaddressesIfyouarewritinganIPv6-enabledclient,you'refacedwiththisquestion:DoyousendoutanIPv6packetordoyousendoutanIPv4packetYouaregivennoguaranteeabouttheunderlyingnetwork.
ThenextmachineyoucontacttogetthisconnectioncanbeanIPv6machine,anIPv4machine,oradualhost.
Let'sassumethattheapplicationsresponsibleforroutingtheconnectionsarecapableofknowingwhetherthenextmachineisanIPv6machineoranIPv4machine.
Inthiscase,itwouldbereallyhelpfulifwecouldhaveIPv6addressesthatcancontainIPv4addressesinsidethem.
Itwouldbegoodtohaveamechanism(theffff.
inmappedv4addresses)totellusiftheaddressisreferringtoapureIPv4node;thiswouldhelpusmakeappropriatedecisionsastowhichtypeofpacketistobesent.
Ourdiscussioninthefinalsectionshouldmakethisclearer.
ibm.
com/developerWorks/developerWorksWritingasimpleIPv6programPage7of11PortingIPv4applicationstoIPv6HerearesomethingstoconsiderwhenportinganIPv4applicationtoIPv6:Thesockaddr_in6structureandthein6_addrstructure,whichcanhold128bitaddresses,havebeendefined.
CheckifyouareusingtherelevantIPv6structure.
INADDR_ANYandINADDR_LOOPBACKmustbemodifiedtoin6addr_anyorin6addr_loopbackforassignments.
TheIN6ADDR_ANY_INITorIN6ADDR_LOOPBACK_INITmacroscanbehelpful.
UseAF_INET6insteadofAF_INET.
NotetherearestructuresandprogramsthatwillworkforIPv6andIPv4.
Oneofthelinkspointstoportingexamplesandthislinkcanbereferredto(see"MovingtoIPv6"inRelatedtopics).
NotethatnochangeinthesyntaxisnecessarywhenusingcertainfunctionsforIPv6.
Theonlydifferencewhenusingthesefunctionsisthatyoumustcastsockaddr_in6tostructsockaddr*.
ThefollowingmacrosandfunctionsareusedtowriteIPv6-enabledapplications:TheIN6_IS_ADDR_V4MAPPEDcanbeusedtodeterminewhetheranIPv6addressisanIPv4-mappedaddress.
gethostbynameretrievesanetworkhostentryviaitsnameandaddressfamily.
getaddrinforeturnsaddressinformationrelatedtoaspecifiedservicelocation.
getnameinforeturnsthetextstringsassociatedwiththesuppliedIPaddressandportnumber.
inet_ptonconvertsthespecifiedaddressintextformtoitsbinaryequivalent.
inet_ntopconvertsthespecifiedbinaryaddressintoatextequivalentthat'ssuitableforpresentation.
getaddrinfoandgetnameinfocanbothbeusedtoretrieveinformationrelatedtoIPv4andIPv6addresses.
inet_ptonandinet_ntopcanbothconvertIPv4andIPv6addresses.
Thismeansthatin"IPv6-ready"applications,youdonotneedtouseeitherinet_addrorinet_ntoa.
ThefollowingfunctionsdonotrequireachangeinsyntaxwhenusedforIPv6:bind,connect,sendmsg,sendto,accept,recvfrom,recvmsg,getpeername,andgetsockname,althoughthecodeforthesefunctionshasbeenmodified.
WritingasimpleIPv6clientLet'snowtakealookatthelogicbehindwritinganIPv6-enabledclient.
Ibelieveweareequippedwiththebasics.
WeknowaboutIPv6addresses.
Wewillbeabletorecognisethemifweseethemindifferentrepresentations.
WewillbeabletoautoconfigureanIPv6addressonourmachineusingautoconf.
Wealsoknowaboutthemappedaddresstransitionmechanismandhaveanideaofthefunctionstouse.
ConsiderthefollowingIPv4client:#include#include#include#include#include.
.
.
developerWorksibm.
com/developerWorks/WritingasimpleIPv6programPage8of11main(argc,argv)/*clientside*/intargc;char*argv[];{structsockaddr_inserver;structservent*sp;structhostent*hp;ints;.
.
.
sp=getservbyname("login","tcp");if(sp==NULL){fprintf(stderr,"rlogin:tcp/login:unknownservice\n");exit(1);}hp=gethostbyname(argv[1]);if(hp==NULL){fprintf(stderr,"rlogin:%s:unknownhost\n",argv[1]);exit(2);}memset((char*)&server,0,sizeof(server));memcpy((char*)&server.
sin_addr,hp->h_addr,hp->h_length);server.
sin_len=sizeof(server);server.
sin_family=hp->h_addrtype;server.
sin_port=sp->s_port;s=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);if(s0){//noteinet_ptonwilltakecareofsettingtheaddress.
.
.
.
.
ip6.
sin6_family=AF_INET6;ip6.
sin6_len=sizeof(structsockaddr_in6);.
.
.
.
.
developerWorksibm.
com/developerWorks/WritingasimpleIPv6programPage10of11}else{//nowitsnotav6addressorav4addresssoitshouldbehostname//doav6lookup,notethatav6lookupwilllookforav6addressifnot//presentitcanpickupav4address//resinitisdefinedinresolv.
hres_init();_res.
options|=RES_USE_INET6;hptr=gethostbyname(name);.
.
.
.
.
//checkhptr->h_addrtypeifitsAF_INET6youcancopytheaddressdirectly//ifnotyouneedtomapit.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
if(connect(sd,&ip6,sizeof(ip6<0){//connectfailure.
.
.
.
}else{//continuewiththeprogram.
}SummaryoftheabovelogicTosummarizethelogic,wechecktoseeifwegotadottedIPv4addresstohandle.
Ifso,wegoaheadandmapitandfillinanIPv6structure,tobeusedbytheconnectcalllater.
Ifit'sanIPv6address,wecopyitdirectlytotheIPv6structure.
Ifit'sahostname,wetryanddoanIPv6lookup.
WecangetanIPv4oranIPv6address.
Weknowthisfromthefamilyfield.
Accordingly,weeithermapitorcopyit,thendoasingleconnectcallregardlessofwhetherit'sanIPv4oranIPv6address,andproceedwithourprogram.
ConclusionWehavelookedonlyattheconceptsweneedtowritetheaboveprogram.
Therearemanymoreinterestingconceptsthatwillsoonbecomepartofeverydaylife.
TherearecontroversiesandconstructivedebatesaboutthingslikeDNSforIPv6andstatefulautoconfigurationforIPv6(DHCP).
Thesetopics,alongwithothers,suchasimplementationofotherlayers,howroutingwillbedone,andhowautoconfigurationwillbeimplemented,willmakeforinterestingdiscussion.
IhopetoseeyousooninamoreexcitingIPv6world!
ibm.
com/developerWorks/developerWorksWritingasimpleIPv6programPage11of11RelatedtopicsIPNextGenerationOverview,byRobertMHinden,givesabriefoverviewofalltheIPngconcepts.
KameprojectisajointeffortofsevencompaniesinJapanthatprovideafreeIPv6andIPsec(forbothIPv4andIPv6)stackforBSDvariants.
6boneisanIPv6testbedtoassistintheevolutionanddeploymentofIPv6.
IPv6draftsandRFCscanbefoundinIPngCurrentSpecifications.
Theygivealltherequireddetailsinaclearandlogicalorder.
StatelessautoconfigurationisdefinedinRFC2462:IPv6StatelessAddressAutoconfiguration.
RFC2893,TransitionMechanismsforIPv6HostsandRouters,specifiesIPv4compatibilitymechanismsthatcanbeimplementedbyIPv6hostsandrouters.
AdditionalinformationonNATcanbefoundinRFC1631,TheIPNetworkAddressTranslator(NAT).
Formorein-depthoverviewsofCIDR,readRFC1517,RFC1518,RFC1519,andRFC1520.
FindouthowIPv6forOS/390providesanimplementationofIPv4andIPv6forOS/390.
Planningforgrowth,fromIBM'sHighVolumeWebSiteTeam,canshowyouhowyourWebsitecansatisfyfuturedemandsandevaluatepotentialworkloadandinfrastructurechanges.
IBM'sPatternsfore-businesssitefeaturesanumberofreusableassetsthatcanhelpspeedtheprocessofdevelopingapplications.
BrowsemoreWebarchitectureresourcesondeveloperWorks.
CopyrightIBMCorporation2001(www.
ibm.
com/legal/copytrade.
shtml)Trademarks(www.
ibm.
com/developerworks/ibm/trademarks/)
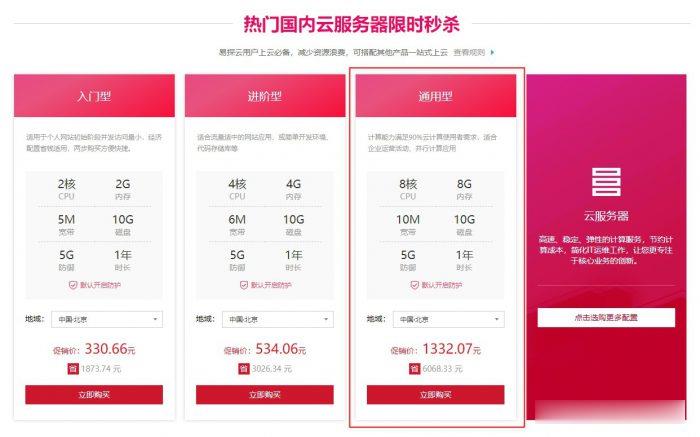
易探云(QQ音乐绿钻)北京/深圳云服务器8核8G10M带宽低至1332.07元/年起
易探云怎么样?易探云香港云服务器比较有优势,他家香港BGP+CN2口碑不错,速度也很稳定。尤其是今年他们动作很大,推出的香港云服务器有4个可用区价格低至18元起,试用过一个月的用户基本会续费,如果年付的话还可以享受8.5折或秒杀价格。今天,云服务器网(yuntue.com)小编推荐一下易探云国内云服务器优惠活动,北京和深圳这二个机房的云服务器2核2G5M带宽低至330.66元/年,还有高配云服务器...
CheapWindowsVPS$4.5/月,美国VPS/免费Windows系统/1Gbps不限流量/,可选美洲、欧洲、亚洲等8大机房
国外商家提供Windows系统的并不常见,CheapWindowsVPS 此次提供的 2 款 VPS 促销套餐,提供 5 折永久优惠码,优惠后月付 4.5 美元起,价格还是挺诱人的,VPS 不限流量,接入 1Gbps 带宽,8 个机房皆可选,其中洛杉矶机房还提供亚洲优化网络供选择,操作系统有 Windows 10 专业版、2012 R2、2016、Linux等。Cheap Windows VPS是...
ProfitServer$34.56/年,西班牙vps、荷兰vps、德国vps/不限制流量/支持自定义ISO
profitserver怎么样?profitserver是一家成立于2003的主机商家,是ITC控股的一个部门,主要经营的产品域名、SSL证书、虚拟主机、VPS和独立服务器,机房有俄罗斯、新加坡、荷兰、美国、保加利亚,VPS采用的是KVM虚拟架构,硬盘采用纯SSD,而且最大的优势是不限制流量,大公司运营,机器比较稳定,数据中心众多。此次ProfitServer正在对德国VPS(法兰克福)、西班牙v...

29ff.com为你推荐
-
2020双十一成绩单2020双十一尾款如何合并付款?原代码什么叫源代码,源代码有什么作用seo优化工具SEO优化工具哪个好用点啊?www.5any.comwww.qbo5.com 这个网站要安装播放器dadi.tvApple TV是干嘛的?怎么用?多少钱?www.175qq.com最炫的qq分组bk乐乐bk乐乐和CK是什么关系?邯郸纠风网河北邯郸有几个县个名单非法集资长房娇人物描写片段,不用太长,150字左右,要有出处!急!!!!!www.mm.com找几个有美女图片的网址